Collapsing Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Viral Infections
- PMID: 35095882
- PMCID: PMC8792967
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.800074
Collapsing Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Viral Infections
Abstract
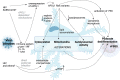
Collapsing glomerulopathy represents a special variant of the proteinuric kidney disease focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Histologically, the collapsing form of FSGS (cFSGS) is characterized by segmental or global condensation and obliteration of glomerular capillaries, the appearance of hyperplastic and hypertrophic podocytes and severe tubulointerstitial damage. Clinically, cFSGS patients present with acute kidney injury, nephrotic-range proteinuria and are at a high risk of rapid progression to irreversible kidney failure. cFSGS can be attributed to numerous etiologies, namely, viral infections like HIV, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr-Virus, and parvovirus B19 and also drugs and severe ischemia. Risk variants of the APOL1 gene, predominantly found in people of African descent, increase the risk of developing cFSGS. Patients infected with the new Corona-Virus SARS-CoV-2 display an increased rate of acute kidney injury (AKI) in severe cases of COVID-19. Besides hemodynamic instability, cytokine mediated injury and direct viral entry and infection of renal epithelial cells contributing to AKI, there are emerging reports of cFSGS associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients of mainly African ethnicity. The pathogenesis of cFSGS is proposed to be linked with direct viral infection of podocytes, as described for HIV-associated glomerulopathy. Nevertheless, there is growing evidence that the systemic inflammatory cascade, activated in acute viral infections like COVID-19, is a major contributor to the impairment of basic cellular functions in podocytes. This mini review will summarize the current knowledge on cFSGS associated with viral infections with a special focus on the influence of systemic immune responses and potential mechanisms propagating the development of cFSGS.
Keywords: APOL 1; COVAN; HIVAN; Immune response; podocyte.
Copyright © 2022 Muehlig, Gies, Huber and Braun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-associated nephropathy: experimental models.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;169:270-285. doi: 10.1159/000320212. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21252526
-
Collapsing and non-collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in kidney transplants.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006 Sep;21(9):2607-14. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl225. Epub 2006 May 16. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006. PMID: 16705026
-
A prospective study of collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Ren Fail. 2016 Jul;38(6):894-8. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2016.1164063. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Ren Fail. 2016. PMID: 27266801
-
An Update on Viral Infection-Associated Collapsing Glomerulopathy.Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024 Jul;31(4):317-325. doi: 10.1053/j.akdh.2023.12.007. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024. PMID: 39084757 Review.
-
Infection-Related Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Children.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7351964. doi: 10.1155/2016/7351964. Epub 2016 May 17. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27294131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
APOL1 and APOL1-Associated Kidney Disease: A Common Disease, an Unusual Disease Gene - Proceedings of the Henry Shavelle Professorship.Glomerular Dis. 2023 Jan 25;3(1):75-87. doi: 10.1159/000529227. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Glomerular Dis. 2023. PMID: 37113494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers to predict organ morbidity in COVID-19: A repository based proteomics perspective.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 Sep;35:101493. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101493. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37304132 Free PMC article.
-
Monogenic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: A conceptual framework for identification and management of a heterogeneous disease.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022 Sep;190(3):377-398. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31990. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35894442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis is involved in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 14;13(1):22250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49697-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38097813 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019-associated nephropathy in an African American patient: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2023 Apr 7;17(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13256-023-03888-z. J Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37024977 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous