Electronic cigarette exposure causes vascular endothelial dysfunction due to NADPH oxidase activation and eNOS uncoupling
- PMID: 35089811
- PMCID: PMC8917923
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00460.2021
Electronic cigarette exposure causes vascular endothelial dysfunction due to NADPH oxidase activation and eNOS uncoupling
Abstract
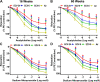
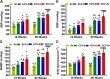
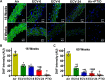
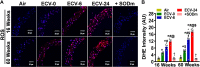
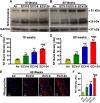
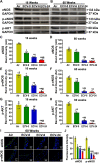
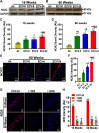
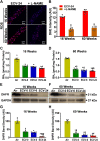
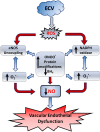
We recently reported a mouse model of chronic electronic cigarette (e-cig) exposure-induced cardiovascular pathology, where long-term exposure to e-cig vape (ECV) induces cardiac abnormalities, impairment of endothelial function, and systemic hypertension. Here, we delineate the underlying mechanisms of ECV-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED), a central trigger of cardiovascular disease. C57/BL6 male mice were exposed to ECV generated from e-cig liquid containing 0, 6, or 24 mg/mL nicotine for 16 and 60 wk. Time-dependent elevation in blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance were observed, along with an impairment of acetylcholine-induced aortic relaxation in ECV-exposed mice, compared with air-exposed control. Decreased intravascular nitric oxide (NO) levels and increased superoxide generation with elevated 3-nitrotyrosine levels in the aorta of ECV-exposed mice were observed, indicating that ECV-induced superoxide reacts with NO to generate cytotoxic peroxynitrite. Exposure increased NADPH oxidase expression, supporting its role in ECV-induced superoxide generation. Downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression and Akt-dependent eNOS phosphorylation occurred in the aorta of ECV-exposed mice, indicating that exposure inhibited de novo NO synthesis. Following ECV exposure, the critical NOS cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin was decreased, with a concomitant loss of its salvage enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase. NADPH oxidase and NOS inhibitors abrogated ECV-induced superoxide generation in the aorta of ECV-exposed mice. Together, our data demonstrate that ECV exposure activates NADPH oxidase and uncouples eNOS, causing a vicious cycle of superoxide generation and vascular oxidant stress that triggers VED and hypertension with predisposition to other cardiovascular disease.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Underlying mechanisms of e-cig-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction are delineated. e-cig exposure activates and increases expression of NADPH oxidase and disrupts activation and coupling of eNOS, leading to a vicious cycle of superoxide generation and peroxynitrite formation, with tetrahydrobiopterin depletion, causing loss of NO that triggers vascular endothelial dysfunction. This process is progressive, increasing with the duration of e-cig exposure, and is more severe in the presence of nicotine, but observed even with nicotine-free vaping.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; e-cigarettes; eNOS uncoupling; tetrahydrobiopterin; vascular endothelial dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic cigarette smoke exposure triggers a vicious cycle of leukocyte and endothelial-mediated oxidant stress that results in vascular dysfunction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Jul 1;319(1):H51-H65. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00657.2019. Epub 2020 May 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32412791 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term electronic cigarette exposure induces cardiovascular dysfunction similar to tobacco cigarettes: role of nicotine and exposure duration.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):H2112-H2129. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00997.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33606584 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling of endothelial nitric oxidase synthase by hypochlorous acid: role of NAD(P)H oxidase-derived superoxide and peroxynitrite.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Dec;26(12):2688-95. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000249394.94588.82. Epub 2006 Oct 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006. Retraction in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022 Nov;42(11):e289. doi: 10.1161/ATV.0000000000000157. PMID: 17023679 Retracted.
-
Malfunction of vascular control in lifestyle-related diseases: mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in the insulin-resistant state.J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Dec;96(4):401-5. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj04006x4. Epub 2004 Dec 15. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15599093 Review.
-
Vascular Redox Signaling, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling, and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Setting of Transportation Noise Exposure or Chronic Treatment with Organic Nitrates.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 May;38(13-15):1001-1021. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0006. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36719770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
E-cigarette effects on vascular function in animals and humans.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Jul;475(7):783-796. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02813-z. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 37084087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tobacco cigarette smoking induces cerebrovascular dysfunction followed by oxidative neuronal injury with the onset of cognitive impairment.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 Jan;45(1):48-65. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241270415. Epub 2024 Aug 13. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 39136181 Free PMC article.
-
The role of acrolein for E-cigarette vapour condensate mediated activation of NADPH oxidase in cultured endothelial cells and macrophages.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Jul;475(7):807-821. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02825-9. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 37285062 Free PMC article.
-
E-Cigarette Aerosol Condensate Leads to Impaired Coronary Endothelial Cell Health and Restricted Angiogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 28;24(7):6378. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076378. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047355 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of chronic electronic cigarette use on endothelial dysfunction measured by flow-mediated vasodilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Tob Induc Dis. 2024 May 22;22. doi: 10.18332/tid/186932. eCollection 2024. Tob Induc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38779295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43: 109–142, 1991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

