Metformin promotes histone deacetylation of optineurin and suppresses tumour growth through autophagy inhibition in ocular melanoma
- PMID: 35075807
- PMCID: PMC8787022
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.660
Metformin promotes histone deacetylation of optineurin and suppresses tumour growth through autophagy inhibition in ocular melanoma
Abstract
Objective: To explore the therapeutic potential and the underlying mechanism of metformin, an adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase (AMPK) activator, in ocular melanoma.
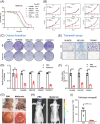
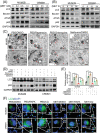
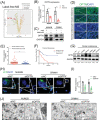
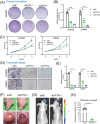
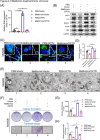
Methods: CCK8, transwell, and colony formation assays were performed to detect the proliferation and migration ability of ocular melanoma cells. A mouse orthotopic xenograft model was built to detect ocular tumor growth in vivo. Western blot, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy were adopted to evaluate the autophagy levels of ocular melanoma cells, and high-throughput proteomics and CUT & Tag assays were performed to analyze the candidate for autophagy alteration.
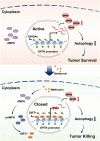
Results: Here, we revealed for the first time that a relatively low dose of metformin induced significant tumorspecific inhibition of the proliferation and migration of ocular melanoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Intriguingly, we found that metformin significantly attenuated autophagic influx in ocular melanoma cells. Through high-throughput proteomics analysis, we revealed that optineurin (OPTN), which is a key candidate for autophagosome formation and maturation, was significantly downregulated after metformin treatment. Moreover, excessive OPTN expression was associated with an unfavorable prognosis of patients. Most importantly, we found that a histone deacetylase, SIRT1, was significantly upregulated after AMPK activation, resulting in histone deacetylation in the OPTN promoter.
Conclusions: Overall, we revealed for the first time that metformin significantly inhibited the progression of ocular melanoma, and verified that metformin acted as an autophagy inhibitor through histone deacetylation of OPTN. This study provides novel insights into metformin - guided suppression of ocular melanoma and the potential mechanism underlying the dual role of metformin in autophagy regulation.
Keywords: OPTN; autophagy; histone modification; metformin; ocular melanoma.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppression of optineurin impairs the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating mitophagy.Cancer Med. 2021 Mar;10(5):1501-1514. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3519. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33600074 Free PMC article.
-
Optineurin promotes autophagosome formation by recruiting the autophagy-related Atg12-5-16L1 complex to phagophores containing the Wipi2 protein.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 5;293(1):132-147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.801944. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29133525 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy receptor OPTN (optineurin) regulates mesenchymal stem cell fate and bone-fat balance during aging by clearing FABP3.Autophagy. 2021 Oct;17(10):2766-2782. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1839286. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33143524 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging views of OPTN (optineurin) function in the autophagic process associated with disease.Autophagy. 2022 Jan;18(1):73-85. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1908722. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 33783320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Selective Autophagy Receptor Optineurin in Crohn's Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 10;9:766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00766. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29692785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetes and skin cancers: Risk factors, molecular mechanisms and impact on prognosis.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Nov 6;10(31):11214-11225. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11214. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36387789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Autophagy in Human Uveal Melanoma and the Development of Potential Disease Biomarkers and Novel Therapeutic Paradigms.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 19;12(2):462. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020462. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMTDB: A comprehensive database of autophagic modulators for anti-tumor drug discovery.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 9;13:956501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.956501. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36016573 Free PMC article.
-
ERCC1 Overexpression Increases Radioresistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 30;14(19):4798. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194798. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230725 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the prognosis of intraocular malignancy: Interventions for association mechanisms between cancer and diabetes.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 8;12:958170. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.958170. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36003786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Espada L, Dakhovnik A, Chaudhari P, et al. Loss of metabolic plasticity underlies metformin toxicity in aged Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Metab. 2020;2(11):1316‐1331. - PubMed
-
- Chang C, Su H, Zhang D, et al. AMPK‐dependent phosphorylation of GAPDH triggers Sirt1 activation and is necessary for autophagy upon glucose starvation. Mol Cell. 2015;60(6):930‐940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
