Impact of intrarectal chromofungin treatment on dendritic cells-related markers in different immune compartments in colonic inflammatory conditions
- PMID: 35068859
- PMCID: PMC8704268
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i47.8138
Impact of intrarectal chromofungin treatment on dendritic cells-related markers in different immune compartments in colonic inflammatory conditions
Abstract
Background: Chromofungin (CHR: chromogranin-A 47-66) is a chromogranin-A derived peptide with anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties. Ulcerative colitis (UC) is characterized by a colonic decrease of CHR and a dysregulation of dendritic CD11c+ cells.
Aim: To investigate the association between CHR treatment and dendritic cells (DCs)-related markers in different immune compartments in colitis.
Methods: A model of acute UC-like colitis using dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) was used in addition to biopsies collected from UC patients.
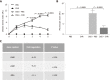
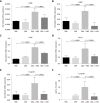
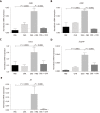
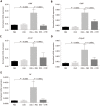
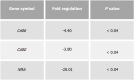
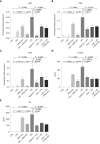
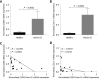
Results: Intrarectal CHR treatment reduced the severity of DSS-induced colitis and was associated with a significant decrease in the expression of CD11c, CD40, CD80, CD86 and interleukin (IL)-12p40 in the inflamed colonic mucosa and CD11c, CD80, CD86 IL-6 and IL-12p40 within the mesenteric lymph nodes and the spleen. Furthermore, CHR treatment decreased CD80 and CD86 expression markers of splenic CD11c+ cells and decreased NF-κB expression in the colon and of splenic CD11c+ cells. In vitro, CHR decreased CD40, CD80, CD86 IL-6 and IL-12p40 expression in naïve bone marrow-derived CD11c+ DCs stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Pharmacological studies demonstrated an impact of CHR on the NF-κB pathway. In patients with active UC, CHR level was reduced and showed a negative linear relationship with CD11c and CD86.
Conclusion: CHR has protective properties against intestinal inflammation via the regulation of DC-related markers and CD11c+ cells. CHR could be a potential therapy of UC.
Keywords: Chromofungin; Chromogranin-A; Colitis; Cytokines; Dendritic cells; Gut hormones.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Bernstein CN has been on the advisory boards for Abbvie Canada, Amgen Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb Canada, Janssen Canada, Roche Canada, Sandoz Canada, Takeda Canada, Pfizer Canada and consulted to Takeda and Mylan Pharmaceuticals. He has received educational grants from Abbvie Canada, Pfizer Canada, Takeda Canada, Janssen Canada. He has been on speaker’s panel for Abbvie Canada, Medtronic Canada and Janssen Canada. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromofungin (CHR: CHGA47-66) is downregulated in persons with active ulcerative colitis and suppresses pro-inflammatory macrophage function through the inhibition of NF-κB signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 1;145:102-113. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.08.013. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28827109
-
Chromofungin Ameliorates the Progression of Colitis by Regulating Alternatively Activated Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2017 Sep 15;8:1131. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01131. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28951733 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppressive effects via human intestinal dendritic cells of probiotic bacteria and steroids in the treatment of acute ulcerative colitis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010 Aug;16(8):1286-98. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21222. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010. PMID: 20155842 Clinical Trial.
-
CD40 and CD86 upregulation with divergent CMRF44 expression on blood dendritic cells in inflammatory bowel diseases.Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Oct;96(10):2946-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.04686.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11693331
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin inhibits the activity and function of dendritic cells through the TLR4/IRAK4/NF-κB signalling pathway.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023;27(3):182-189. doi: 10.5114/wo.2023.133741. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023. PMID: 38239865 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of Chromofungin in oligomeric amyloid β42 (Aβ42)-induced toxicity in neurons in Alzheimer's disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 24;16(10):9216-9227. doi: 10.18632/aging.205865. Epub 2024 May 24. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38795392 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Multifunctional Antimicrobial Peptides as Immunomodulatory and Anticancer Therapy: Chromogranin A-Derived Peptides and Dermaseptins as Endogenous versus Exogenous Actors.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 22;14(10):2014. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102014. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic cells: the yin and yang in disease progression.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1321051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1321051. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38239364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranin A: An Endocrine Factor of Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 5;24(5):4986. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054986. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

