The omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern does not readily infect Syrian hamsters
- PMID: 35066015
- PMCID: PMC8776349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105253
The omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern does not readily infect Syrian hamsters
Abstract
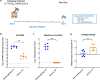
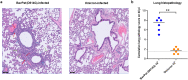
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VoCs) has exacerbated the COVID-19 pandemic. End of November 2021, a new SARS-CoV-2 variant namely the omicron (B.1.1.529) emerged. Since this omicron variant is heavily mutated in the spike protein, WHO classified this variant as the 5th variant of concern (VoC). We previously demonstrated that the ancestral strain and the other SARS-CoV-2 VoCs replicate efficiently in and cause a COVID19-like pathology in Syrian hamsters. We here wanted to explore the infectivity of the omicron variant in comparison to the ancestral D614G strain in the hamster model. Strikingly, in hamsters that had been infected with the omicron variant, a 3 log10 lower viral RNA load was detected in the lungs as compared to animals infected with D614G and no infectious virus was detectable in this organ. Moreover, histopathological examination of the lungs from omicron-infected hamsters revealed no signs of peri-bronchial inflammation or bronchopneumonia.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hamsters; Infectivity; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2 VoC.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.5.5 and BQ.1.1 Omicron variants in mice and hamsters.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0062823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00628-23. Epub 2023 Sep 7. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37676002 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (R346K) variant in Syrian hamsters and its cross-neutralization with different variants of concern.EBioMedicine. 2022 May;79:103997. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103997. Epub 2022 Apr 8. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35405385 Free PMC article.
-
Prototype and BA.5 protein nanoparticle vaccines protect against Omicron BA.5 variant in Syrian hamsters.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0120623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01206-23. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38305154 Free PMC article.
-
The emergence and epidemic characteristics of the highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant.J Med Virol. 2022 Jun;94(6):2376-2383. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27643. Epub 2022 Feb 11. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 35118687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omicron: What Makes the Latest SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern So Concerning?J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0207721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02077-21. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35225672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis and virulence of coronavirus disease: Comparative pathology of animal models for COVID-19.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2316438. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2316438. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38362881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2: An Updated Review Highlighting Its Evolution and Treatments.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;10(12):2145. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122145. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus causes attenuated infection and disease in mice and hamsters.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Dec 29:rs.3.rs-1211792. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1211792/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: Nature. 2022 Mar;603(7902):687-692. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04441-6. PMID: 34981044 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Immunogenicity and efficacy of vaccine boosters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.5 in male Syrian hamsters.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 17;14(1):4260. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40033-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37460536 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience of S309 and AZD7442 monoclonal antibody treatments against infection by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineage strains.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 2;13(1):3824. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31615-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35780162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelnabi R., Boudewijns R., Foo C.S., Seldeslachts L., Sanchez-Felipe L., Zhang X., Delang L., Maes P., Kaptein S.J.F., Weynand B., Vande Velde G., Neyts J., Dallmeier K. Comparing infectivity and virulence of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants in Syrian hamsters. EBioMedicine. 2021;68:103403. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103403. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdelnabi R., Foo C.S., Jochmans D., Vangeel L., De Jonghe S., Augustijns P., Mols R., Weynand B., Wattanakul T., Hoglund R.M., Tarning J., Mowbray C.E., Sjö P., Escudié F., Scandale I., Chatelain E., Neyts J. The oral protease inhibitor (PF-07321332) protects Syrian hamsters against infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. bioRxiv. 2021;2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.11.04.467077. 11.04.467077. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bentley E.G., Kirby A., Sharma P., Kipar A., Mega D.F., Bramwell C., Penrice-Randal R., Prince T., Brown J.C., Zhou J., Screaton G.R., Barclay W.S., Owen A., Hiscox J.A., Stewart J.P. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 Variant leads to less severe disease than Pango B and Delta variants strains in a mouse model of severe COVID-19. bioRxiv. 2021;2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.12.26.474085. 12.26.474085. - DOI
-
- Boudewijns R., Thibaut H.J., Kaptein S.J.F., Li R., Vergote V., Seldeslachts L., Van Weyenbergh J., De Keyzer C., Bervoets L., Sharma S., Liesenborghs L., Ma J., Jansen S., Van Looveren D., Vercruysse T., Wang X., Jochmans D., Martens E., Roose K., De Vlieger D., Schepens B., Van Buyten T., Jacobs S., Liu Y., Martí-Carreras J., Vanmechelen B., Wawina-Bokalanga T., Delang L., Rocha-Pereira J., Coelmont L., Chiu W., Leyssen P., Heylen E., Schols D., Wang L., Close L., Matthijnssens J., Van Ranst M., Compernolle V., Schramm G., Van Laere K., Saelens X., Callewaert N., Opdenakker G., Maes P., Weynand B., Cawthorne C., Vande Velde G., Wang Z., Neyts J., Dallmeier K. STAT2 signaling restricts viral dissemination but drives severe pneumonia in SARS-CoV-2 infected hamsters. Nat. Commun. 2020;11 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19684-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chi-wai M., et al. Press release; 2021. HKUMed Finds Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Can Infect Faster and Better than Delta in Human Bronchus but with Less Severe Infection in Lung.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

