Effects of antibiotic treatment on microbiota, viral transmission and viral pathogenesis of MoMuLV ts1 infected BALB/c mice
- PMID: 35061714
- PMCID: PMC8782509
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261689
Effects of antibiotic treatment on microbiota, viral transmission and viral pathogenesis of MoMuLV ts1 infected BALB/c mice
Abstract
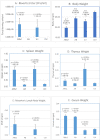
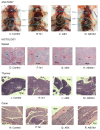
The effects of normal and altered intestinal microbiota on murine retroviral transmission via the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) are diverse. The role of orally administered antibiotic treatment (ABX) on viral transmission, GIT microbial dysbiosis and subsequent pathogenesis of Moloney Murine Leukemia virus-temperature sensitive 1 (ts1) on BALB/c mice were studied. BALB/c mice were divided into four groups: ABXts1-Treatment/Infection;ABX-Treatment/No infection;ts1-No treatment/Infection;Ctrl (control)-No treatment/No infection. ABXts1 and ABX groups showed a significant phylogenetic shift (ANOSIM p-value = 0.001) in alpha and beta diversity comparisons for microbial community composition compared to Ctrl group. Mice in the ABXts1 and ABX groups showed megacolon compared to ts1 and Ctrl groups; ABXts1 and ts1 groups showed hepatosplenomegaly, thymus enlargement, and mesenteric lymphadenopathy compared to ABX and Ctrl groups. Ctrl group had no abnormal manifestations. ABX treatment and ts1 infection uniquely affect microbial community when compared to control: ABXts1 and ABX groups significantly reduce microbiome diversity by over 80% and ts1 group by over 30%. ABXts1 and ts1 groups' viral load and clinical manifestations of infection were comparable; antibiotic treatment did not notably affect ts1 infection. Transmission and pathophysiology of ts1 infection were not significantly altered by the microbial composition of the GI tract, but ts1 viral infection did result in microbial dysbiosis independent of antibiotic treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A small animal model for mother-to-fetus transmission of ts1, a murine retrovirus.Viral Immunol. 2003;16(2):191-201. doi: 10.1089/088282403322017929. Viral Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12828870
-
Astrocytes survive chronic infection and cytopathic effects of the ts1 mutant of the retrovirus Moloney murine leukemia virus by upregulation of antioxidant defenses.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(7):3273-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.7.3273-3284.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16537594 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of Jab1, HIF-1alpha, and VEGF by Moloney murine leukemia virus-ts1 infection: a possible cause of neurodegeneration.J Neurovirol. 2008 May;14(3):239-51. doi: 10.1080/13550280802093919. J Neurovirol. 2008. PMID: 18569458
-
Tsl and LP-BM5: a comparison of two murine retrovirus models for HIV.Viral Immunol. 2001;14(2):95-109. doi: 10.1089/088282401750234475. Viral Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11398815 Review.
-
Antibiotic-induced dysbiosis effects on the murine gastrointestinal tract and their systemic repercussions.Life Sci. 2018 Aug 15;207:480-491. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.06.030. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30056862 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

