Lipid Nanoparticles for the Posterior Eye Segment
- PMID: 35056986
- PMCID: PMC8779178
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010090
Lipid Nanoparticles for the Posterior Eye Segment
Abstract
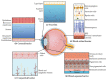
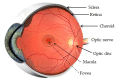
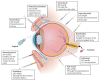
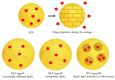
This review highlights the application of lipid nanoparticles (Solid Lipid Nanoparticles, Nanostructured Lipid Carriers, or Lipid Drug Conjugates) as effective drug carriers for pathologies affecting the posterior ocular segment. Eye anatomy and the most relevant diseases affecting the posterior segment will be summarized. Moreover, preparation methods and different types and subtypes of lipid nanoparticles will also be reviewed. Lipid nanoparticles used as carriers to deliver drugs to the posterior eye segment as well as their administration routes, pharmaceutical forms and ocular distribution will be discussed emphasizing the different targeting strategies most recently employed for ocular drug delivery.
Keywords: NLC; SLN; drug transport; lipid nanoparticles; ocular barriers; ocular drug delivery; posterior segment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cutting-edge advances in therapy for the posterior segment of the eye: Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers.Int J Pharm. 2020 Nov 15;589:119831. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119831. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32877729 Review.
-
Application of lipid nanoparticles to ocular drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016 Dec;13(12):1743-1757. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1201059. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27291069 Review.
-
A review of nanocarrier-mediated drug delivery systems for posterior segment eye disease: challenges analysis and recent advances.J Drug Target. 2021 Aug;29(7):687-702. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2021.1878366. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Drug Target. 2021. PMID: 33474998 Review.
-
Formulations based on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for cutaneous use: A review.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Jan 15;112:159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.11.023. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29183800 Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC): Overcoming the anatomical and physiological barriers of the eye - Part I - Barriers and determining factors in ocular delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017 Jan;110:70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.10.009. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017. PMID: 27789358 Review.
Cited by
-
Innovative Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery Systems for Advanced Treatment of Posterior Segment Ocular Diseases.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(32):e2403399. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403399. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39031809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diclofenac Loaded Biodegradable Nanoparticles as Antitumoral and Antiangiogenic Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 28;15(1):102. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010102. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678731 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated Drug Delivery to Posterior Segment of Eye and their In-vivo Successes.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(6):713-723. doi: 10.2174/1389201025666230907145019. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37691214 Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticle technology-mediated therapeutic gene manipulation in the eyes.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jun 3;35(3):102236. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102236. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39005878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Medicine with Lipid-Based Nanosystems-The Successful Case of Liposomes.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 2;11(2):435. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020435. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keeffe J., Resnikoff S. Innovative Approaches in the Delivery of Primary and Secondary Eye Care. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2019. Prevalence and Causes of Vision Impairment and Blindness: The Global Burden of Disease; pp. 7–20.
-
- Sánchez-López E., Espina M., Doktorovova S., Souto E.B., García M.L. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC): Overcoming the anatomical and physiological barriers of the eye—Part I—Barriers and determining factors in ocular delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017;110:70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.10.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

