Scaffolding of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling by β-Arrestins
- PMID: 35055186
- PMCID: PMC8778048
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23021000
Scaffolding of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling by β-Arrestins
Abstract
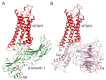
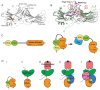
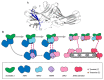
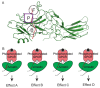
β-arrestins were initially identified to desensitize and internalize G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Receptor-bound β-arrestins also initiate a second wave of signaling by scaffolding mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling components, MAPK kinase kinase, MAPK kinase, and MAPK. In particular, β-arrestins facilitate ERK1/2 or JNK3 activation by scaffolding signal cascade components such as ERK1/2-MEK1-cRaf or JNK3-MKK4/7-ASK1. Understanding the precise molecular and structural mechanisms of β-arrestin-mediated MAPK scaffolding assembly would deepen our understanding of GPCR-mediated MAPK activation and provide clues for the selective regulation of the MAPK signaling cascade for therapeutic purposes. Over the last decade, numerous research groups have attempted to understand the molecular and structural mechanisms of β-arrestin-mediated MAPK scaffolding assembly. Although not providing the complete mechanism, these efforts suggest potential binding interfaces between β-arrestins and MAPK signaling components and the mechanism for MAPK signal amplification by β-arrestin-mediated scaffolding. This review summarizes recent developments of cellular and molecular works on the scaffolding mechanism of β-arrestin for MAPK signaling cascade.
Keywords: MAPK; arrestin; protein structure; scaffold.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scaffolding mechanism of arrestin-2 in the cRaf/MEK1/ERK signaling cascade.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 14;118(37):e2026491118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026491118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34507982 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor sequestration in response to β-arrestin-2 phosphorylation by ERK1/2 governs steady-state levels of GPCR cell-surface expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 15;112(37):E5160-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508836112. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26324936 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction at GPCRs: Allosteric activation of the ERK MAPK by β-arrestin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Oct 24;120(43):e2303794120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2303794120. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37844230 Free PMC article.
-
Many faces of the GPCR-arrestin interaction.Arch Pharm Res. 2020 Sep;43(9):890-899. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01263-w. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 32803684 Review.
-
The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Jul;69(3):256-297. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013367. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28626043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging therapies for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with a focus on cAMP signaling.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 2;9:981963. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.981963. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36120538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical physiology of phosphoinositide rapid dynamics and regulation in living cells.J Gen Physiol. 2022 Jun 6;154(6):e202113074. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202113074. Epub 2022 May 18. J Gen Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35583815 Free PMC article.
-
Domperidone, a Dopamine Receptor D2 Antagonist, Induces Apoptosis by Inhibiting the ERK/STAT3-Mediated Pathway in Human Colon Cancer HCT116 Cells.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024 Sep 1;32(5):568-576. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.048. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38914471 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptor molecules mediate negative regulation of macrophage inflammatory pathways: a closer look.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1355012. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1355012. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38482001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Neurokinin-1 Receptor Signaling Pathways with Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(39):6460-6486. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230818110812. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37594106 Review.
References
-
- Thomsen A.R.B., Plouffe B., Cahill T.J., 3rd, Shukla A.K., Tarrasch J.T., Dosey A.M., Kahsai A.W., Strachan R.T., Pani B., Mahoney J.P., et al. GPCR-G Protein-beta-Arrestin Super-Complex Mediates Sustained G Protein Signaling. Cell. 2016;166:907–919. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

