Frequency and Spectrum of Mutations Induced by Gamma Rays Revealed by Phenotype Screening and Whole-Genome Re-Sequencing in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 35054839
- PMCID: PMC8775868
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020654
Frequency and Spectrum of Mutations Induced by Gamma Rays Revealed by Phenotype Screening and Whole-Genome Re-Sequencing in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
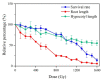
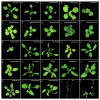
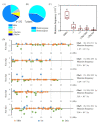
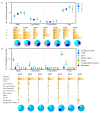
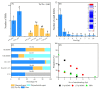
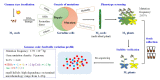
Genetic variations are an important source of germplasm diversity, as it provides an allele resource that contributes to the development of new traits for plant breeding. Gamma rays have been widely used as a physical agent for mutation creation in plants, and their mutagenic effect has attracted extensive attention. However, few studies are available on the comprehensive mutation profile at both the large-scale phenotype mutation screening and whole-genome mutation scanning. In this study, biological effects on M1 generation, large-scale phenotype screening in M2 generation, as well as whole-genome re-sequencing of seven M3 phenotype-visible lines were carried out to comprehensively evaluate the mutagenic effects of gamma rays on Arabidopsis thaliana. A total of 417 plants with visible mutated phenotypes were isolated from 20,502 M2 plants, and the phenotypic mutation frequency of gamma rays was 2.03% in Arabidopsis thaliana. On average, there were 21.57 single-base substitutions (SBSs) and 11.57 small insertions and deletions (InDels) in each line. Single-base InDels accounts for 66.7% of the small InDels. The genomic mutation frequency was 2.78 × 10-10/bp/Gy. The ratio of transition/transversion was 1.60, and 64.28% of the C > T events exhibited the pyrimidine dinucleotide sequence; 69.14% of the small InDels were located in the sequence with 1 to 4 bp terminal microhomology that was used for DNA end rejoining, while SBSs were less dependent on terminal microhomology. Nine genes, on average, were predicted to suffer from functional alteration in each re-sequenced line. This indicated that a suitable mutation gene density was an advantage of gamma rays when trying to improve elite materials for one certain or a few traits. These results will aid the full understanding of the mutagenic effects and mechanisms of gamma rays and provide a basis for suitable mutagen selection and parameter design, which can further facilitate the development of more controlled mutagenesis methods for plant mutation breeding.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; gamma rays; mutation; phenotype screening; whole-genome re-sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma-rays induced genome wide stable mutations in cowpea deciphered through whole genome sequencing.Int J Radiat Biol. 2024;100(7):1072-1084. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2024.2345087. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Int J Radiat Biol. 2024. PMID: 38683196
-
Genetic polymorphisms in mutagenesis progeny of Arabidopsis thaliana irradiated by carbon-ion beams and γ-rays irradiations.Int J Radiat Biol. 2020 Feb;96(2):267-275. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1688412. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020. PMID: 31692404
-
Identification and Characterization of γ-Ray-Induced Mutations in Rice Cytoplasmic Genomes by Whole-Genome Sequencing.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2020;160(2):100-109. doi: 10.1159/000506033. Epub 2020 Mar 7. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2020. PMID: 32146470
-
Linking genotype to phenotype using the Arabidopsis unimutant collection.Plant J. 2010 Mar;61(6):928-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04119.x. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20409268 Review.
-
The art and design of genetic screens: Arabidopsis thaliana.Nat Rev Genet. 2002 Feb;3(2):124-36. doi: 10.1038/nrg730. Nat Rev Genet. 2002. PMID: 11836506 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultra-high static magnetic field induces a change in the spectrum but not frequency of DNA spontaneous mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Dec 6;14:1305069. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1305069. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38126008 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of seed and seedling irradiation with gamma rays and carbon ions for mutation induction in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Apr 6;14:1149083. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1149083. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37089645 Free PMC article.
-
Morphometric frequency and spectrum of gamma-ray-induced chlorophyll mutants identified by phenotype and development of novel variants in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.).PLoS One. 2023 Jun 12;18(6):e0286975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286975. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37307261 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of phylogenetic relationships and genetic diversity of Sagittaria trifolia using phenotypic traits and SNP markers.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 3;19(6):e0302313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302313. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38829862 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis for the gamma-ray-induced sweetpotato mutants with altered stem growth pattern.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 31;15:1419399. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1419399. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39144719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin Y.F., Nagasawa H., Little J.B., Kato T.A., Shih H.Y., Xie X.J., Wilson P.F., Brogan J.R., Kurimasa A., Chen D.J., et al. Differential radiosensitivity phenotypes of DNA-PKcs mutations affecting NHEJ and HRR systems following irradiation with gamma-rays or very low fluences of alpha particles. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e93579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093579. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2018B020206002/Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province
- 11975285; 12135016/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- none/Crop Varietal Improvement and Insect Pests Control by Nuclear Radiation
- Y201974/Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS
- Y9HIRFL200/the User Project of National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator of Lanzhou
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

