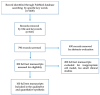
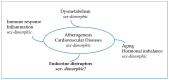
Environmental Contaminants Acting as Endocrine Disruptors Modulate Atherogenic Processes: New Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Women?
- PMID: 35053192
- PMCID: PMC8773563
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12010044
Environmental Contaminants Acting as Endocrine Disruptors Modulate Atherogenic Processes: New Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Women?
Abstract
The number of aged individuals is increasing worldwide, rendering essential the comprehension of pathophysiological mechanisms of age-related alterations, which could facilitate the development of interventions contributing to "successful aging" and improving quality of life. Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) include pathologies affecting the heart or blood vessels, such as hypertension, peripheral artery disease and coronary heart disease. Indeed, age-associated modifications in body composition, hormonal, nutritional and metabolic factors, as well as a decline in physical activity are all involved in the increased risk of developing atherogenic alterations that raise the risk of CVD development. Several factors have been reported to play a role in the alterations observed in muscle and endothelial cells and that lead to increased CVD, such as genetic pattern, smoking and unhealthy lifestyle. Moreover, a difference in the risk of these diseases in women and men has been reported. Interestingly, in the past decades attention has been focused on a potential role of several pollutants that disrupt human health by interfering with hormonal pathways, and more specifically in non-communicable diseases such as obesity, diabetes and CVD. This review will focus on the potential alteration induced by Endocrine Disruptors (Eds) in the attempt to characterize a potential role in the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the atheromatous degeneration process and CVD progression.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; bisphenol A; cadmium; cardiovascular diseases; endocrine disruptors; inflammatory cytokines; women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between environmental endocrine disruptors and cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Environ Res. 2020 Aug;187:109464. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109464. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 32438096
-
Endocrine Disruptors Leading to Obesity and Related Diseases.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Oct 24;14(10):1282. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14101282. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29064461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cadmium exposure alters steroid receptors and proinflammatory cytokine levels in endothelial cells in vitro: a potential mechanism of endocrine disruptor atherogenic effect.J Endocrinol Invest. 2019 Jun;42(6):727-739. doi: 10.1007/s40618-018-0982-1. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019. PMID: 30478740
-
Cardiovascular disease risk factors induce mesenchymal features and senescence in mouse cardiac endothelial cells.Elife. 2021 Mar 4;10:e62678. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62678. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33661096 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental endocrine disruption of energy metabolism and cardiovascular risk.Curr Diab Rep. 2014 Jun;14(6):494. doi: 10.1007/s11892-014-0494-0. Curr Diab Rep. 2014. PMID: 24756343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The endocrine disruptor cadmium modulates the androgen-estrogen receptors ratio and induces inflammatory cytokines in luminal (A) cell models of breast cancer.Endocrine. 2024 Mar;83(3):798-809. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03594-2. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 37979099 Free PMC article.
-
Biomolecules and Cardiovascular Diseases in Women.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 24;12(12):1750. doi: 10.3390/biom12121750. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551178 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Vascular System in Degenerative Diseases: Mechanisms and Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 11;25(4):2169. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042169. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Bioinformatics-Gene Network Approach Reveals Linkage between Estrogenic Endocrine Disruptors and Vascular Remodeling in Peripheral Arterial Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 19;25(8):4502. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084502. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piepoli M.F., Abreu A., Albus C., Ambrosetti M., Brotons C., Catapano A.L., Corra U., Cosyns B., Deaton C., Graham I. Update on cardiovascular prevention in clinical practice: A position paper of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020;27:181–205. doi: 10.1177/2047487319893035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous