Differential target multiplexed spinal cord stimulation programming modulates proteins involved in ion regulation in an animal model of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 35048719
- PMCID: PMC8785327
- DOI: 10.1177/17448069211060181
Differential target multiplexed spinal cord stimulation programming modulates proteins involved in ion regulation in an animal model of neuropathic pain
Abstract
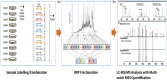
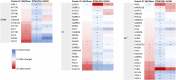
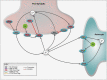
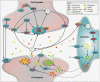
The effect of spinal cord stimulation (SCS) using differential target multiplexed programming (DTMP) on proteins involved in the regulation of ion transport in spinal cord (SC) tissue of an animal model of neuropathic pain was evaluated in comparison to low rate (LR) SCS. Rats subjected to the spared nerve injury model (SNI) and implanted with a SCS lead were assigned to DTMP or LR and stimulated for 48 h. A No-SCS group received no stimulation, and a Sham group received no SNI or stimulation. Proteins in the dorsal ipsilateral quadrant of the stimulated SC were identified and quantified using mass spectrometry. Proteins significantly modulated by DTMP or LR relative to No-SCS were identified. Bioinformatic tools were used to identify proteins related to ion transport regulation. DTMP modulated a larger number of proteins than LR. More than 40 proteins significantly involved in the regulation of chloride (Cl-), potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), or calcium (Ca2+) ions were identified. SNI affected proteins that promote the increase of intracellular Ca2+, Na+, and K+ and decrease of intracellular Cl-. DTMP modulated proteins involved in glial response to neural injury that affect Ca2+ signaling. DTMP decreased levels of proteins related to Ca2+ transport that may result in the reduction of intracellular Ca2+. Presynaptic proteins involved in GABA vesicle formation and release were upregulated by DTMP. DTMP also upregulated postsynaptic proteins involved with elevated intracellular Cl-, while modulating proteins, expressed by astrocytes, that regulate postsynaptic Cl- inhibition. DTMP downregulated K+ regulatory proteins affected by SNI that affect neuronal depolarization, and upregulated proteins that are associated with a decrease of intracellular neuronal K+ and astrocyte uptake of extracellular K+. DTMP treatment modulated the expression of proteins with the potential to facilitate a reversal of dysregulation of ion transport and signaling associated with a model of neuropathic pain.
Keywords: differential target multiplexed programming; ion transport regulation; neuropathic pain model; proteomics; spinal cord stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of Neuroinflammation via mTOR Pathway is Disparately Regulated by Differential Target Multiplexed and Traditional Low-Rate Spinal Cord Stimulation in a Neuropathic Pain Model.J Pain Res. 2022 Sep 13;15:2857-2866. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S378490. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36156899 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Changes of MAPK-Related Inflammatory Response in an Animal Model of Neuropathic Pain by Differential Target Multiplexed SCS and Low-Rate SCS.J Pain Res. 2022 Apr 1;15:895-907. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S348738. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35392631 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of stimulation intensity of a differential target multiplexed SCS program in an animal model of neuropathic pain.Pain Pract. 2023 Jul;23(6):639-646. doi: 10.1111/papr.13235. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Pain Pract. 2023. PMID: 37067033
-
Modulation of Glia-Mediated Processes by Spinal Cord Stimulation in Animal Models of Neuropathic Pain.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 14;2:702906. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2021.702906. eCollection 2021. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 35295479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal Cord Stimulation Paradigms and Pain Relief: A Preclinical Systematic Review on Modulation of the Central Inflammatory Response in Neuropathic Pain.Neuromodulation. 2023 Jan;26(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2022.04.049. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Neuromodulation. 2023. PMID: 35931643 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Expression of Extracellular Matrix Proteins by Differential Target Multiplexed Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) and Traditional Low-Rate SCS in a Rat Nerve Injury Model.Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 31;12(4):537. doi: 10.3390/biology12040537. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106738 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Neuroinflammation via mTOR Pathway is Disparately Regulated by Differential Target Multiplexed and Traditional Low-Rate Spinal Cord Stimulation in a Neuropathic Pain Model.J Pain Res. 2022 Sep 13;15:2857-2866. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S378490. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36156899 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative review of current neuromodulation modalities for spinal cord injury.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 9;4:1143405. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1143405. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36969918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine racemase interaction with N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors antagonist reveals potential alternative target of chronic pain treatment: Molecular docking study.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2022 Jul-Sep;13(3):232-237. doi: 10.4103/japtr.japtr_72_22. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2022. PMID: 35935687 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Changes of MAPK-Related Inflammatory Response in an Animal Model of Neuropathic Pain by Differential Target Multiplexed SCS and Low-Rate SCS.J Pain Res. 2022 Apr 1;15:895-907. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S348738. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35392631 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

