Targeting Stress-Response Pathways and Therapeutic Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer
- PMID: 35048023
- PMCID: PMC8757684
- DOI: 10.3389/froh.2021.676643
Targeting Stress-Response Pathways and Therapeutic Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
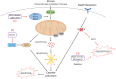
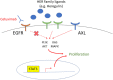
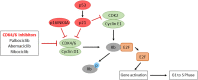
Head and neck cancer is the sixth leading cancer worldwide; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) accounts for more than 90% of incident cases. In the US, cases of HNSCC associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) have been growing in proportion amongst a younger demographic with superior outcomes to the same treatments, relative to cases associated with tobacco. Yet failures to improve the long-term prognosis of advanced HNSCC over the last three decades persist in part due to intrinsic and acquired mechanisms of resistance. Deregulation of the pathways to respond to stress, such as apoptosis and autophagy, often contributes to drug resistance and tumor progression. Here we review the stress-response pathways in drug response and resistance in HNSCC to explore strategies to overcome these resistance mechanisms. We focus on the mechanisms of resistance to current standard cares, such as chemotherapy (i.e., cisplatin), radiation, and cetuximab. Then, we discuss the strategies to overcome these resistances, including novel combinations and immunotherapy.
Keywords: chemotherapy; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; oxidative stress; radiotherapy; resistance; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Bos, Ratti and Harada.
Conflict of interest statement
JAR is a part of Light Switch Bio, LLC., a startup company that is developing light-based therapeutics and diagnostics for commercial applications, including the treatment of cancers. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy in stages III and IV head and neck cancer.Curr Oncol. 2010 Jun;17(3):37-48. doi: 10.3747/co.v17i3.520. Curr Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20567625 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous targeting of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 by afatinib overcomes intrinsic and acquired cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.Mol Oncol. 2018 Jun;12(6):830-854. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12197. Epub 2018 May 1. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29603584 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab-Containing Combinations in Locally Advanced and Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2019 May 20;9:383. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00383. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31165040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Medicine Approaches to Overcome Resistance to Therapy in Head and Neck Cancers.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:614332. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.614332. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New advances into cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous carcinoma: Mechanisms and therapeutic aspects.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114778. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114778. Epub 2023 May 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37137185 Review.
Cited by
-
Cisplatin-induced HSF1-HSP90 axis enhances the expression of functional PD-L1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(4):4605-4615. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5310. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36200687 Free PMC article.
-
Association between spatial distribution of leukocyte subsets and clinical presentation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 23;14:1240394. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1240394. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38322012 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR Mutations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 30;23(7):3818. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073818. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma: connecting the dots to move forward.Front Oral Health. 2024 Sep 4;5:1461022. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1461022. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39296524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual role of autophagy in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jan 31;150(2):56. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05514-3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38291202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

