Aromatase in the Human Brain
- PMID: 35024691
- PMCID: PMC8744447
- DOI: 10.1089/andro.2021.0007
Aromatase in the Human Brain
Abstract
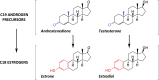
The aromatase cytochrome P450 (P450arom) enzyme, or estrogen synthase, which is coded by the CYP19A1 gene, is widely expressed in a subpopulation of excitatory and inhibitory neurons, astrocytes, and other cell types in the human brain. Experimental studies in laboratory animals indicate a prominent role of brain aromatization of androgens to estrogens in regulating different brain functions. However, the consequences of aromatase expression in the human brain remain poorly understood. Here, we summarize the current knowledge about aromatase expression in the human brain, abundant in the thalamus, amygdala, hypothalamus, cortex, and hippocampus and discuss its role in the regulation of sensory integration, body homeostasis, social behavior, cognition, language, and integrative functions. Since brain aromatase is affected by neurodegenerative conditions and may participate in sex-specific manifestations of autism spectrum disorders, major depressive disorder, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease, we discuss future avenues for research and potential clinical and therapeutic implications of the expression of aromatase in the human brain.
Keywords: aging; amygdala; cerebral cortex; hippocampus; hypothalamus; thalamus.
© Iñigo Azcoitia et al., 2021; Published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sex differences in distribution and identity of aromatase gene expressing cells in the young adult rat brain.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Sep 1;14(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00541-8. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37658400 Free PMC article.
-
Androgens regulate aromatase cytochrome P450 messenger ribonucleic acid in rat brain.Endocrinology. 1994 Jul;135(1):395-401. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.1.8013375. Endocrinology. 1994. PMID: 8013375
-
Anatomic relationships between aromatase and androgen receptor mRNA expression in the hypothalamus and amygdala of adult male cynomolgus monkeys.J Comp Neurol. 2001 Oct 15;439(2):208-23. doi: 10.1002/cne.1343. J Comp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11596049
-
A review of brain aromatase cytochrome P450.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996 Jun;22(1):1-26. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1996. PMID: 8871783 Review.
-
Brain aromatization of androgens.J Reprod Med. 1994 Apr;39(4):257-61. J Reprod Med. 1994. PMID: 8040841 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in distribution and identity of aromatase gene expressing cells in the young adult rat brain.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Sep 1;14(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00541-8. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37658400 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and Translational Regulation of Differentially Expressed Genes in Yucatan Miniswine Brain Tissues following Traumatic Brain Injury.J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2024;7(1):81-91. doi: 10.26502/jbsb.5107080. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 38818113 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and Brain: The Role of Sex Chromosomes and Hormones in Brain Development and Parkinson's Disease.Cells. 2023 May 27;12(11):1486. doi: 10.3390/cells12111486. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37296608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complexity of Sex Differences and Their Impact on Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 24;11(5):1261. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051261. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of androgen receptor expression and activity in the mouse brain.Sci Rep. 2024 May 15;14(1):11115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61733-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38750183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naftolin F, Ryan KJ, Petro Z. Aromatization of androstenedione by the diencephalon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971;33(2):368–370. - PubMed
-
- Naftolin F, Ryan KJ, Petro Z. Aromatization of androstenedione by limbic system tissue from human foetuses. J Endocrinol. 1971;51(4):795–796. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Segura LM. Aromatase in the brain: Not just for reproduction anymore. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008;20(6):705–712. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
