Low RUFY3 expression level is associated with lymph node metastasis in older women with invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 35018543
- PMCID: PMC8844209
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-021-06482-3
Low RUFY3 expression level is associated with lymph node metastasis in older women with invasive breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Sentinel lymph node biopsy is omitted in older women (≥ 70 years old) with clinical lymph node (LN)-negative hormone receptor-positive breast cancer as it does not influence adjuvant treatment decision-making. However, older women are heterogeneous in frailty while the chance of recurrence increase with improving longevity. Therefore, a biomarker that identifies LN metastasis may facilitate treatment decision-making. RUFY3 is associated with cancer progression. We evaluated RUFY3 expression level as a biomarker for LN-positive breast cancer in older women.
Methods: Clinical and transcriptomic data of breast cancer patients were obtained from the Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium (METABRIC, n = 1903) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA, n = 1046) Pan-cancer study cohorts.
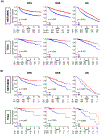
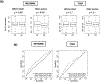
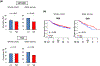
Results: A total of 510 (METABRIC) and 211 (TCGA) older women were identified. LN-positive breast cancer, which represented 51.4% (METABRIC) and 48.4% (TCGA), demonstrated worse disease-free, disease-specific, and overall survival. RUFY3 levels were significantly lower in LN-positive tumors regardless of age. The area under the curve for the receiver operator characteristic (AUC-ROC) curves showed RUFY3-predicted LN metastasis. Low RUFY3 enriched oxidative phosphorylation, DNA repair, MYC targets, unfolded protein response, and mtorc1 signaling gene sets, was associated with T helper type 1 cell infiltration, and with intratumor heterogeneity and fraction altered. Low RUFY3 expression was associated with LN-positive breast cancer and with worse disease-specific survival among older women.
Conclusion: Older women with breast cancers who had low expression level of RUFY3 were more frequently diagnosed with LN-positive tumors, which translated into worse prognosis.
Keywords: Axillary lymph node; Breast cancer; Geriatric oncology; RUFY3.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
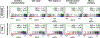

Similar articles
-
[Optimal treatment of the axilla after positive sentinel lymph node biopsy in early invasive breast cancer. Early results of the OTOASOR trial].Orv Hetil. 2013 Dec 8;154(49):1934-42. doi: 10.1556/OH.2013.29765. Orv Hetil. 2013. PMID: 24292111 Clinical Trial. Hungarian.
-
Impact of sentinel lymph node biopsy by ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy for patients with suspicious node positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2018 Jan;25(1):86-93. doi: 10.1007/s12282-017-0795-7. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28735457
-
Sentinel node biopsy versus low axillary sampling in women with clinically node negative operable breast cancer.Breast. 2013 Dec;22(6):1081-6. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Breast. 2013. PMID: 23948301 Clinical Trial.
-
Sentinel lymph node as a new marker for therapeutic planning in breast cancer patients.J Surg Oncol. 2004 Mar;85(3):102-11. doi: 10.1002/jso.20022. J Surg Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14991881 Review.
-
Management of the axilla in patients with breast cancer and positive sentinel lymph node biopsy: An evidence-based update in a European breast center.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020 Jan;46(1):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.08.013. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31445768 Review.
Cited by
-
RUFY3 regulates endolysosomes perinuclear positioning, antigen presentation and migration in activated phagocytes.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 18;14(1):4290. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40062-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37463962 Free PMC article.
-
circSORBS1 inhibits lung cancer progression by sponging miR-6779-5p and directly binding RUFY3 mRNA.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 24;22(1):590. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05423-0. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38915053 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced cancer cell proliferation and aggressive phenotype counterbalance in breast cancer with high BRCA1 gene expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Nov;208(2):321-331. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07421-8. Epub 2024 Jul 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38972017 Free PMC article.
-
miR-3133 is an unfavorable prognosis factor and tumor suppressor in colon cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Apr 20;23(2):132. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01059-3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37079151
-
Diagnostic value of core needle biopsy for determining HER2 status in breast cancer, especially in the HER2-low population.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan;197(1):189-200. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06781-3. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36346486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Breast cancer facts & figures 2019–2020. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society, Inc; 2019.
-
- Lodi M, Scheer L, Reix N, et al. (2017) Breast cancer in elderly women and altered clinico-pathological characteristics: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 166:657–668. - PubMed
-
- Kiderlen M, de Glas NA, Bastiaannet E, et al. (2014) Impact of comorbidity on outcome of older breast cancer patients: a FOCUS cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 145:185–192. - PubMed
-
- Muss HB, Berry DA, Cirrincione C, et al. (2007) Toxicity of older and younger patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy for node positive breast cancer: the cancer and Leukemia group B experience. J Clin Oncol 25:3699–3704. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA248018/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA248018/US National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute grant
- R01CA250412/US National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute grant
- R01CA160688/US National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

