Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prevention and Progression through the Modulation of the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 35010954
- PMCID: PMC8746460
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14010079
Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Prevention and Progression through the Modulation of the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
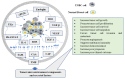
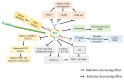
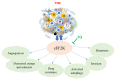
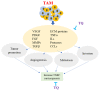
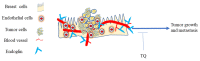
To date, the tumor microenvironment (TME) has gained considerable attention in various areas of cancer research due to its role in driving a loss of immune surveillance and enabling rapid advanced tumor development and progression. The TME plays an integral role in driving advanced aggressive breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), a pivotal mediator for tumor cells to communicate with the surrounding cells via lymphatic and circulatory systems. Furthermore, the TME plays a significant role in all steps and stages of carcinogenesis by promoting and stimulating uncontrolled cell proliferation and protecting tumor cells from the immune system. Various cellular components of the TME work together to drive cancer processes, some of which include tumor-associated adipocytes, fibroblasts, macrophages, and neutrophils which sustain perpetual amplification and release of pro-inflammatory molecules such as cytokines. Thymoquinone (TQ), a natural chemical component from black cumin seed, is widely used traditionally and now in clinical trials for the treatment/prevention of multiple types of cancer, showing a potential to mitigate components of TME at various stages by various pathways. In this review, we focus on the role of TME in TNBC cancer progression and the effect of TQ on the TME, emphasizing their anticipated role in the prevention and treatment of TNBC. It was concluded from this review that the multiple components of the TME serve as a critical part of TNBC tumor promotion and stimulation of uncontrolled cell proliferation. Meanwhile, TQ could be a crucial compound in the prevention and progression of TNBC therapy through the modulation of the TME.
Keywords: breast cancer; thymoquinone; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor-microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor microenvironment: Challenges and opportunities in targeting metastasis of triple negative breast cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Mar;153:104683. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104683. Epub 2020 Feb 9. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32050092 Review.
-
Insights into the Targeting Potential of Thymoquinone for Therapeutic Intervention Against Triple-negative Breast Cancer.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(1):70-80. doi: 10.2174/1389450118666170612095959. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28606050 Review.
-
Current Advancements of Plant-Derived Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy through Deregulating Cancer Cell Functions and Reprogramming Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13571. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413571. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnic disparities in the immune microenvironment of triple negative breast cancer and its role in therapeutic outcomes.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Sep;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e1779. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1779. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 36632988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone Inhibition of Chemokines in TNF-α-Induced Inflammatory and Metastatic Effects in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 8;24(12):9878. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129878. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373025 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anticancer Effects of Thymoquinone through the Antioxidant Activity, Upregulation of Nrf2, and Downregulation of PD-L1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 13;14(22):4787. doi: 10.3390/nu14224787. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432484 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of the Chemoresistance Gene BIRC5 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 22;14(21):5180. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215180. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358602 Free PMC article.
-
Coating of chitosan on poly D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid thymoquinone nanoparticles enhances the anti-tumor activity in triple-negative breast cancer.Front Chem. 2023 Feb 8;11:1044953. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1044953. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36846852 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphyllin II inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Dec;30(6):224. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13348. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39364737 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Adipocytes and Breast Cancer: Intertwining in the Tumor Microenvironment and Challenges for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 24;15(3):726. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030726. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu C., Feng Q., Yang H., Wang G., Huang L., Ba Q., Zhang C., Wang Y., Chen Y., Cheng Q., et al. A Light-Triggered Mesenchymal Stem Cell Delivery System for Photoacoustic Imaging and Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2018;5:1800382. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800382. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

