AU-Rich Element RNA Binding Proteins: At the Crossroads of Post-Transcriptional Regulation and Genome Integrity
- PMID: 35008519
- PMCID: PMC8744917
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23010096
AU-Rich Element RNA Binding Proteins: At the Crossroads of Post-Transcriptional Regulation and Genome Integrity
Abstract
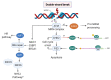
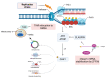
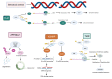
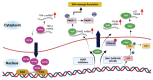
Genome integrity must be tightly preserved to ensure cellular survival and to deter the genesis of disease. Endogenous and exogenous stressors that impose threats to genomic stability through DNA damage are counteracted by a tightly regulated DNA damage response (DDR). RNA binding proteins (RBPs) are emerging as regulators and mediators of diverse biological processes. Specifically, RBPs that bind to adenine uridine (AU)-rich elements (AREs) in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of mRNAs (AU-RBPs) have emerged as key players in regulating the DDR and preserving genome integrity. Here we review eight established AU-RBPs (AUF1, HuR, KHSRP, TIA-1, TIAR, ZFP36, ZFP36L1, ZFP36L2) and their ability to maintain genome integrity through various interactions. We have reviewed canonical roles of AU-RBPs in regulating the fate of mRNA transcripts encoding DDR genes at multiple post-transcriptional levels. We have also attempted to shed light on non-canonical roles of AU-RBPs exploring their post-translational modifications (PTMs) and sub-cellular localization in response to genotoxic stresses by various factors involved in DDR and genome maintenance. Dysfunctional AU-RBPs have been increasingly found to be associated with many human cancers. Further understanding of the roles of AU-RBPS in maintaining genomic integrity may uncover novel therapeutic strategies for cancer.
Keywords: Adenine-Uridine rich element; DNA damage response; RNA binding proteins; cancer; genome stability; oncogenes; post-transcriptional regulation; replication stress; tumour suppressors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of BCL2 mRNA by the RNA-binding protein ZFP36L1 in malignant B cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 11;9(7):e102625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102625. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25014217 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Diseases by RNA-Binding ZFP36 Family Proteins.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;12:711633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711633. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional control of the MCT-1-associated protein DENR/DRP by RNA-binding protein AUF1.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2007 May-Jun;4(3):233-9. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2007. PMID: 17878526
-
Exercise, skeletal muscle and inflammation: ARE-binding proteins as key regulators in inflammatory and adaptive networks.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2015;21:42-57. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25826388 Review.
-
The AU-rich element landscape across human transcriptome reveals a large proportion in introns and regulation by ELAVL1/HuR.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2018 Feb;1861(2):167-177. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2017.12.006. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2018. PMID: 29413897
Cited by
-
RNA-Binding Proteins and Their Emerging Roles in Cancer: Beyond the Tip of the Iceberg.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 1;24(11):9612. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119612. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298567 Free PMC article.
-
KHDRBS1 regulates the pentose phosphate pathway and malignancy of GBM through SNORD51-mediated polyadenylation of ZBED6 pre-mRNA.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Nov 8;15(11):802. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07163-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39516455 Free PMC article.
-
Surmounting Cancer Drug Resistance: New Perspective on RNA-Binding Proteins.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;16(8):1114. doi: 10.3390/ph16081114. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZFP36 loss-mediated BARX1 stabilization promotes malignant phenotypes by transactivating master oncogenes in NSCLC.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 16;14(8):527. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06044-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37587140 Free PMC article.
-
The 3' Untranslated Regions of Ebola Virus mRNAs Contain AU-Rich Elements Involved in Posttranscriptional Stabilization and Decay.J Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 13;228(Suppl 7):S488-S497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad312. J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37551415 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

