Stress Granules in the Anti-Cancer Medications Mechanism of Action: A Systematic Scoping Review
- PMID: 35004322
- PMCID: PMC8739770
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.797549
Stress Granules in the Anti-Cancer Medications Mechanism of Action: A Systematic Scoping Review
Abstract
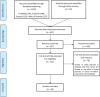
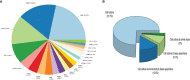
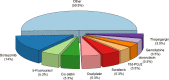
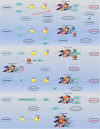
Stress granule (SG) formation is a well-known cellular mechanism for minimizing stress-related damage and increasing cell survival. In addition to playing a critical role in the stress response, SGs have emerged as critical mediators in human health. It seems logical that SGs play a key role in cancer cell formation, development, and metastasis. Recent studies have shown that many SG components contribute to the anti-cancer medications' responses through tumor-associated signaling pathways and other mechanisms. SG proteins are known for their involvement in the translation process, control of mRNA stability, and capacity to function in both the cytoplasm and nucleus. The current systematic review aimed to include all research on the impact of SGs on the mechanism of action of anti-cancer medications and was conducted using a six-stage methodological framework and the PRISMA guideline. Prior to October 2021, a systematic search of seven databases for eligible articles was performed. Following the review of the publications, the collected data were subjected to quantitative and qualitative analysis. Notably, Bortezomib, Sorafenib, Oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, Cisplatin, and Doxorubicin accounted for the majority of the medications examined in the studies. Overall, this systematic scoping review attempts to demonstrate and give a complete overview of the function of SGs in the mechanism of action of anti-cancer medications by evaluating all research.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; anti-cancer medication; bortezomib; cisplatin; doxorubicin; oxaliplatin; sorafenib; stress granule.
Copyright © 2021 Asadi, Moslehian, Sabaie, Poornabi, Ghasemi, Hassani, Hussen, Taheri and Rezazadeh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs.J Vis Exp. 2023 May 26;(195). doi: 10.3791/6561. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37235796
-
Ethics of Procuring and Using Organs or Tissue from Infants and Newborns for Transplantation, Research, or Commercial Purposes: Protocol for a Bioethics Scoping Review.Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Dec 5;9:717. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.23235.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39839977 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Granules Involved in Formation, Progression and Metastasis of Cancer: A Scoping Review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 17;9:745394. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.745394. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34604242 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring conceptual and theoretical frameworks for nurse practitioner education: a scoping review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):146-55. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2150. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571290
-
The effectiveness of school-based family asthma educational programs on the quality of life and number of asthma exacerbations of children aged five to 18 years diagnosed with asthma: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):69-81. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2335. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571284
Cited by
-
Melatonin: Regulation of Viral Phase Separation and Epitranscriptomics in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 23;23(15):8122. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158122. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular impact of mutations in RNA splicing factors in cancer.Mol Cell. 2024 Oct 3;84(19):3667-3680. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.07.019. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39146933 Review.
-
Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Mechanisms, Drug Targets and Approaches to Clinical Translation.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 4;14(7):1826. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071826. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

