Role of Exercise Intensity on Th1/Th2 Immune Modulations During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 35003073
- PMCID: PMC8727446
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761382
Role of Exercise Intensity on Th1/Th2 Immune Modulations During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
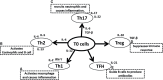
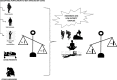
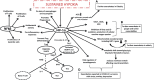
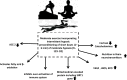
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to several pioneering scientific discoveries resulting in no effective solutions with the exception of vaccination. Moderate exercise is a significant non-pharmacological strategy, to reduce the infection-related burden of COVID-19, especially in patients who are obese, elderly, and with additional comorbidities. The imbalance of T helper type 1 (Th1) or T helper type 2 (Th2) cells has been well documented among populations who have suffered as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, and who are at maximum risk of infection and mortality. Moderate and low intensity exercise can benefit persons at risk from the disease and survivors by favorable modulation in Th1/Th2 ratios. Moreover, in COVID-19 patients, mild to moderate intensity aerobic exercise also increases immune system function but high intensity aerobic exercise may have adverse effects on immune responses. In addition, sustained hypoxia in COVID-19 patients has been reported to cause organ failure and cell death. Hypoxic conditions have also been highlighted to be triggered in COVID-19-susceptible individuals and COVID-19 survivors. This suggests that hypoxia inducible factor (HIF 1α) might be an important focus for researchers investigating effective strategies to minimize the effects of the pandemic. Intermittent hypoxic preconditioning (IHP) is a method of exposing subjects to short bouts of moderate hypoxia interspersed with brief periods of normal oxygen concentrations (recovery). This methodology inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory factors, activates HIF-1α to activate target genes, and subsequently leads to a higher production of red blood cells and hemoglobin. This increases angiogenesis and increases oxygen transport capacity. These factors can help alleviate virus induced cardiopulmonary hemodynamic disorders and endothelial dysfunction. Therefore, during the COVID-19 pandemic we propose that populations should engage in low to moderate exercise individually designed, prescribed and specific, that utilizes IHP including pranayama (yoga), swimming and high-altitude hiking exercise. This would be beneficial in affecting HIF-1α to combat the disease and its severity. Therefore, the promotion of certain exercises should be considered by all sections of the population. However, exercise recommendations and prescription for COVID-19 patients should be structured to match individual levels of capability and adaptability.
Keywords: COVID-19; Th1/Th2 ratio; hypoxia; immunomodulation; intermittent hypoxic preconditioning.
Copyright © 2021 Supriya, Gao, Gu and Baker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elements of Th1/Th2 response and disease severity in COVID-19 patients: A short report.J Med Virol. 2022 Jan;94(1):404-406. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27313. Epub 2021 Sep 4. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34460125 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate and glutamine supplementation modulates the Th1/Th2 balance after exercise performed at a simulated altitude of 4500 m.Nutrition. 2014 Nov-Dec;30(11-12):1331-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.03.019. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Nutrition. 2014. PMID: 25280408 Clinical Trial.
-
T-Helper Cell Subset Response Is a Determining Factor in COVID-19 Progression.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 26;11:624483. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.624483. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33718270 Free PMC article.
-
The concept of type-1 and type-2 helper T cells and their cytokines in humans.Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16(3-4):427-55. doi: 10.3109/08830189809043004. Int Rev Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9505198 Review.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 and asthma, allergic rhinitis: molecular mechanisms and host-environmental interactions.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb 1;21(1):1-7. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000699. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33186186 Review.
Cited by
-
Innate and adaptive immune response in SARS-CoV-2 infection-Current perspectives.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 22;13:1053437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1053437. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36505489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th1-dominant cytokine responses in kidney patients after COVID-19 vaccination are associated with poor humoral responses.NPJ Vaccines. 2023 May 17;8(1):70. doi: 10.1038/s41541-023-00664-4. NPJ Vaccines. 2023. PMID: 37198189 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Inflammation in the Development of COVID-19 to Parkinson's Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2024 May 21;17:3259-3282. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S460161. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38800597 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection and Comorbidities.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 15;12(2):321. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020321. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36839596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted benefits of walking for healthy aging: from Blue Zones to molecular mechanisms.Geroscience. 2023 Dec;45(6):3211-3239. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00873-8. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Geroscience. 2023. PMID: 37495893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Röcken M, Müller KM, Saurat JH, Hauser C. Lectin-Mediated Induction of IL-4-Producing CD4+ T Cells. J Immunol (1991) 146:577–84. - PubMed
-
- Sad S, Mosmann TR. Single IL-2-Secreting Precursor CD4 T Cell Can Develop Into Either Th1 or Th2 Cytokine Secretion Phenotype. J Immunol (1994) 153:3514–22. - PubMed
-
- Szulc B, Piasecki E. Effects of Interferons, Interferon Inducers and Growth Factors on Phagocytosis Measured by Quantitative Determination of Synthetic Compound Ingested by Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) (1988) 36:537–45. - PubMed

