Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptor activation in the hypothalamus recruits unique signaling pathways involved in energy homeostasis
- PMID: 35001657
- PMCID: PMC8897015
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00320.2021
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptor activation in the hypothalamus recruits unique signaling pathways involved in energy homeostasis
Abstract
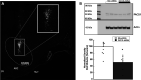
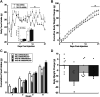
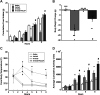
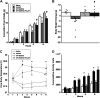
Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) exerts pleiotropic effects on ventromedial nuclei (VMN) of the hypothalamus and its control of feeding and energy expenditure through the type I PAC1 receptor (PAC1R). However, the endogenous role of PAC1Rs in the VMN and the downstream signaling responsible for PACAP's effects on energy balance are unknown. Numerous studies have revealed that PAC1Rs are coupled to both Gαs/adenylyl cyclase/protein kinase A (Gαs/AC/PKA) and Gαq/phospholipase C/protein kinase C (Gαq/PLC/PKC), while also undergoing trafficking following stimulation. To determine the endogenous role of PAC1Rs and downstream signaling that may explain PACAP's pleiotropic effects, we used RNA interference to knockdown VMN PAC1Rs and pharmacologically inhibited PKA, PKC, and PAC1R trafficking. Knocking down PAC1Rs increased meal sizes, reduced total number of meals, and induced body weight gain. Inhibition of either PKA or PKC alone in awake male Sprague-Dawley rats, attenuated PACAP's hypophagic and anorectic effects during the dark phase. However, PKA or PKC inhibition potentiated PACAP's thermogenic effects during the light phase. Analysis of locomotor activity revealed that PKA inhibition augmented PACAP's locomotor effects, whereas PKC inhibition had no effect. Finally, PACAP administration in the VMN induces surface PAC1R trafficking into the cytosol which was blocked by endocytosis inhibitors. Subsequently, inhibition of PAC1R trafficking into the cytosol attenuated PACAP-induced hypophagia. These results revealed that endogenous PAC1Rs uniquely engage PKA, PKC, and receptor trafficking to mediate PACAP's pleiotropic effects in VMN control of feeding and metabolism.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Endogenous PAC1 receptors, integral to VMN management of feeding behavior and body weight regulation, uniquely engage PKA, PKC, and receptor trafficking to mediate the hypothalamic ventromedial nuclei control of feeding and metabolism. PACAP appears to use different signaling mechanisms to regulate feeding behavior from its effects on metabolism.
Keywords: PAC1R; PACAP; energy expenditure; feeding; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stimulation of the hypothalamic ventromedial nuclei by pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide induces hypophagia and thermogenesis.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):R1625-34. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00334.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21957159 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic PACAP/PAC1R Involvement in Feeding and Body Weight Regulation.Endocrinology. 2023 Mar 13;164(5):bqad044. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad044. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 36917637 Review.
-
Intrahypothalamic pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide regulates energy balance via site-specific actions on feeding and metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Dec;305(12):E1452-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00293.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24148346 Free PMC article.
-
PAC1 receptors mediate pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide- and progesterone-facilitated receptivity in female rats.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Nov;19(11):2798-811. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0387. Epub 2005 Jun 23. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15976009
-
PAC1 Receptor Internalization and Endosomal MEK/ERK Activation Is Essential for PACAP-Mediated Neuronal Excitability.J Mol Neurosci. 2021 Aug;71(8):1536-1542. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01821-x. Epub 2021 Mar 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33675454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sexually dimorphic role of the locus coeruleus PAC1 receptors in regulating acute stress-associated energy metabolism.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Oct 5;16:995573. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.995573. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36275856 Free PMC article.
-
Female reproductive functions of the neuropeptide PACAP.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 20;13:982551. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.982551. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36204113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting VIP and PACAP Receptor Signaling: New Insights into Designing Drugs for the PACAP Subfamily of Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 22;23(15):8069. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158069. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897648 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kong L, Albano R, Madayag A, Raddatz N, Mantsch JR, Choi S, Lobner D, Baker DA. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide orchestrates neuronal regulation of the astrocytic glutamate-releasing mechanism system xc (.). J Neurochem 137: 384–393, 2016. doi:10.1111/jnc.13566. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

