Rbfox1 is required for myofibril development and maintaining fiber type-specific isoform expression in Drosophila muscles
- PMID: 34996845
- PMCID: PMC8742874
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202101342
Rbfox1 is required for myofibril development and maintaining fiber type-specific isoform expression in Drosophila muscles
Abstract
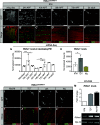
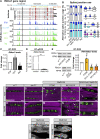
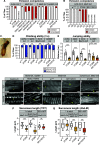
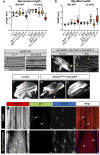
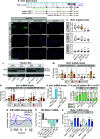
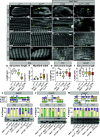
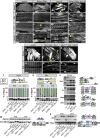
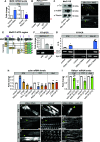
Protein isoform transitions confer muscle fibers with distinct properties and are regulated by differential transcription and alternative splicing. RNA-binding Fox protein 1 (Rbfox1) can affect both transcript levels and splicing, and is known to contribute to normal muscle development and physiology in vertebrates, although the detailed mechanisms remain obscure. In this study, we report that Rbfox1 contributes to the generation of adult muscle diversity in Drosophila Rbfox1 is differentially expressed among muscle fiber types, and RNAi knockdown causes a hypercontraction phenotype that leads to behavioral and eclosion defects. Misregulation of fiber type-specific gene and splice isoform expression, notably loss of an indirect flight muscle-specific isoform of Troponin-I that is critical for regulating myosin activity, leads to structural defects. We further show that Rbfox1 directly binds the 3'-UTR of target transcripts, regulates the expression level of myogenic transcription factors myocyte enhancer factor 2 and Salm, and both modulates expression of and genetically interacts with the CELF family RNA-binding protein Bruno1 (Bru1). Rbfox1 and Bru1 co-regulate fiber type-specific alternative splicing of structural genes, indicating that regulatory interactions between FOX and CELF family RNA-binding proteins are conserved in fly muscle. Rbfox1 thus affects muscle development by regulating fiber type-specific splicing and expression dynamics of identity genes and structural proteins.
© 2022 Nikonova et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bruno 1/CELF regulates splicing and cytoskeleton dynamics to ensure correct sarcomere assembly in Drosophila flight muscles.PLoS Biol. 2024 Apr 29;22(4):e3002575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002575. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38683844 Free PMC article.
-
A Candidate RNAi Screen Reveals Diverse RNA-Binding Protein Phenotypes in Drosophila Flight Muscle.Cells. 2021 Sep 22;10(10):2505. doi: 10.3390/cells10102505. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685485 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein Arrest (Bruno) regulates alternative splicing to enable myofibril maturation in Drosophila flight muscle.EMBO Rep. 2015 Feb;16(2):178-91. doi: 10.15252/embr.201439791. Epub 2014 Dec 22. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 25532219 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental regulation of RNA processing by Rbfox proteins.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Mar;8(2):10.1002/wrna.1398. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1398. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 27748060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Muscleblind family of proteins: an emerging class of regulators of developmentally programmed alternative splicing.Differentiation. 2006 Mar;74(2-3):65-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2006.00060.x. Differentiation. 2006. PMID: 16533306 Review.
Cited by
-
Bruno 1/CELF regulates splicing and cytoskeleton dynamics to ensure correct sarcomere assembly in Drosophila flight muscles.PLoS Biol. 2024 Apr 29;22(4):e3002575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002575. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38683844 Free PMC article.
-
A Candidate RNAi Screen Reveals Diverse RNA-Binding Protein Phenotypes in Drosophila Flight Muscle.Cells. 2021 Sep 22;10(10):2505. doi: 10.3390/cells10102505. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amir-Zilberstein L, Blechman J, Sztainberg Y, Norton WH, Reuveny A, Borodovsky N, Tahor M, Bonkowsky JL, Bally-Cuif L, Chen A, et al. (2012) Homeodomain protein otp and activity-dependent splicing modulate neuronal adaptation to stress. Neuron 73: 279–291. 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.019 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
