LRRK2 and idiopathic Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 34991886
- PMCID: PMC8854345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2021.12.002
LRRK2 and idiopathic Parkinson's disease
Abstract
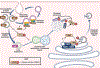
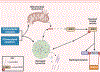
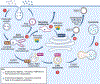
The etiology of idiopathic Parkinson's disease (iPD) is multifactorial, and both genetics and environmental exposures are risk factors. While mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 (LRRK2) that are associated with increased kinase activity are the most common cause of autosomal dominant PD, the role of LRRK2 in iPD, independent of mutations, remains uncertain. In this review, we discuss how the architecture of LRRK2 influences kinase activation and how enhanced LRRK2 substrate phosphorylation might contribute to pathogenesis. We describe how oxidative stress and endolysosomal dysfunction, both of which occur in iPD, can activate non-mutated LRRK2 to a similar degree as pathogenic mutations. Similarly, environmental toxicants that are linked epidemiologically to iPD risk can also activate LRRK2. In aggregate, current evidence suggests an important role for LRRK2 in iPD.
Keywords: autophagy–lysosomal pathway; endogenous protein expression; environmental toxicants; kinase; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests None declared by authors.
Figures
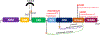
Similar articles
-
LRRK2 activation in idiopathic Parkinson's disease.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Jul 25;10(451):eaar5429. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar5429. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30045977 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2 and the Endolysosomal System in Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2020;10(4):1271-1291. doi: 10.3233/JPD-202138. J Parkinsons Dis. 2020. PMID: 33044192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2, GBA and their interaction in the regulation of autophagy: implications on therapeutics in Parkinson's disease.Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Jan 31;11(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00281-6. Transl Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35101134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in elucidating the function of leucine-rich repeat protein kinase-2 in normal cells and Parkinson's disease.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020 Apr;63:102-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32036294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The G2019S variant of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) alters endolysosomal trafficking by impairing the function of the GTPase RAB8A.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):4738-4758. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005008. Epub 2019 Feb 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30709905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) inhibition upregulates microtubule-associated protein 1B to ameliorate lysosomal dysfunction and parkinsonism.MedComm (2020). 2023 Nov 20;4(6):e429. doi: 10.1002/mco2.429. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38020716 Free PMC article.
-
Novel N-Linked Isoquinoline Amides as LRRK2 Inhibitors for Treating Parkinson's Disease.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022 Jun 21;13(7):1008-1009. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00263. eCollection 2022 Jul 14. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35928851 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Disturb mitochondrial associated proteostasis: Neurodegeneration and imperfect ageing.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 10;11:1146564. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1146564. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36968195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2 kinase inhibition reverses G2019S mutation-dependent effects on tau pathology progression.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Mar 4;13(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00403-2. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 38438877 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2; Communicative Role in the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Overlapping.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(10):1177-1188. doi: 10.2174/0118715273270874231205050727. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38279762 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

