A novel antagonist of TRPM2 and TRPV4 channels: Carvacrol
- PMID: 34989943
- PMCID: PMC8732973
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-021-00887-1
A novel antagonist of TRPM2 and TRPV4 channels: Carvacrol
Abstract
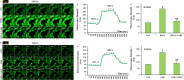
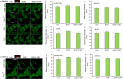
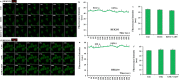
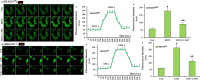
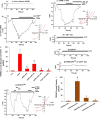
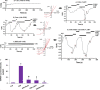
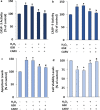
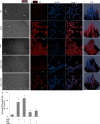
The overload cytosolic free Ca2+ (cCa2+) influx-mediated excessive generation of oxidative stress in the pathophysiological conditions induces neuronal and cellular injury via the activation of cation channels. TRPM2 and TRPV4 channels are activated by oxidative stress, and their specific antagonists have not been discovered yet. The antioxidant and anti-Covid-19 properties of carvacrol (CARV) were recently reported. Hence, I suspected possible antagonist properties of CARV against oxidative stress (OS)/ADP-ribose (ADPR)-induced TRPM2 and GSK1016790A (GSK)-mediated TRPV4 activations in neuronal and kidney cells. I investigated the antagonist role of CARV on the activations of TRPM2 and TRPV4 in SH-SY5Y neuronal, BV-2 microglial, and HEK293 cells. The OS/ADPR and GSK in the cells caused to increase of TRPM2/TRPV4 current densities and overload cytosolic free Ca2+ (cCa2+) influx with an increase of mitochondrial membrane potential, cytosolic (cROS), and mitochondrial (mROS) ROS. The changes were not observed in the absence of TRPM2 and TRPV4 or the presence of Ca2+ free extracellular buffer and PARP-1 inhibitors (PJ34 and DPQ). When OS-induced TRPM2 and GSK-induced TRPV4 activations were inhibited by the treatment of CARV, the increase of cROS, mROS, lipid peroxidation, apoptosis, cell death, cCa2+ concentration, caspase -3, and caspase -9 levels were restored via upregulation of glutathione and glutathione peroxidase. In conclusion, the treatment of CARV modulated the TRPM2 and TRPV4-mediated overload Ca2+ influx and may provide an avenue for protecting TRPM2 and TRPV4-mediated neurodegenerative diseases associated with the increase of mROS and cCa2+. The possible TRPM2 and TRPV4 blocker action of carvacrol (CARV) via the modulation oxidative stress and apoptosis in the SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. TRPM2 is activated by DNA damage-induced (via PARP-1 activation) ADP-ribose (ADPR) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) (H2O2), although it is inhibited by nonspecific inhibitors (ACA and 2-APB). TRPV4 is activated by the treatments of GSK1016790A (GSK), although it is inhibited by a nonspecific inhibitor (ruthenium red, RuRe). The treatment of GSK induces excessive generation of ROS. The accumulation of free cytosolic Ca2+ (cCa2+) via the activations of TRPM2 and TRPV4 in the mitochondria causes the increase of mitochondrial membrane depolarization (ΔΨm). In turn, the increase of ΔΨm causes the excessive generation of ROS. The TRPM2 and TRPV4-induced the excessive generations of ROS result in the increase of apoptosis and cell death via the activations of caspase -3 (Casp-3) and caspase -9 (Casp-9) in the neuronal cells, although their oxidant actions decrease the glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx) levels. The oxidant and apoptotic adverse actions of TRPM2 and TRPV4 are modulated by the treatment of CARV.
Keywords: Carvacrol; Glutathione; Neurodegeneration; Oxidative stress; TRPM2; TRPV4.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRPM2 Channel Inhibition Attenuates Amyloid β42-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in the Hippocampus of Mice.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;43(3):1335-1353. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01253-0. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35840808
-
Selenium prevents interferon-gamma induced activation of TRPM2 channel and inhibits inflammation, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and apoptosis in microglia.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Feb;36(2):285-298. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00624-0. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 33044639
-
Amantadine Attenuated Hypoxia-Induced Mitochondrial Oxidative Neurotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Inflammation via the Inhibition of TRPM2 and TRPV4 Channels.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jun;59(6):3703-3720. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02814-6. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35366734
-
TRPM2 cation channels, oxidative stress and neurological diseases: where are we now?Neurochem Res. 2011 Mar;36(3):355-66. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0347-4. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21140288 Review.
-
The role of TRP channels in oxidative stress-induced cell death.J Membr Biol. 2006 Jan;209(1):31-41. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0839-3. Epub 2006 Apr 17. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16685599 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Properties of Thyme Oil and Its Main Constituents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 8;24(8):6936. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086936. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Modulates Diabetes-Induced Neuropathic Pain, Apoptosis, and Oxidative Neurotoxicity in Mice Through TRPV4 Channel Inhibition.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):7269-7286. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04311-4. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38976129 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing an ANO1-Based Cell Model for High-Throughput Screening Targeting TRPV4 Regulators.Molecules. 2024 Feb 28;29(5):1036. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051036. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474548 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating mitochondrial calcium channels (TRPM2/MCU/NCX) as a therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative disorders.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 20;17:1202167. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1202167. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37928737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of Antiviral Drug Therapy for COVID-19: Where Do We Stand?Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 4;10(11):2815. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112815. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

