Antibacterial polysaccharide-based hydrogel dressing containing plant essential oil for burn wound healing
- PMID: 34988231
- PMCID: PMC8693078
- DOI: 10.1093/burnst/tkab041
Antibacterial polysaccharide-based hydrogel dressing containing plant essential oil for burn wound healing
Abstract
Background: Polysaccharide-based hydrogels have been developed for many years to treat burn wounds. Essential oils extracted from aromatic plants generally exhibit superior biological activity, especially antibacterial properties. Studies have shown that antibacterial hydrogels mixed with essential oils have great potential for burn wound healing. This study aimed to develop an antibacterial polysaccharide-based hydrogel with essential oil for burn skin repair.
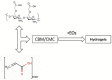
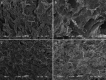
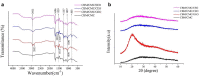
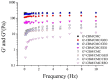
Methods: Eucalyptus essential oil (EEO), ginger essential oil (GEO) and cumin essential oil (CEO) were employed for the preparation of effective antibacterial hydrogels physically crosslinked by carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) and carbomer 940 (CBM). Composite hydrogels were prepared and characterized using antimicrobial activity studies, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, gas chromatography-mass spectrometery, rheological analysis, viscosity, swelling, water loss rate and water vapor transmission rate studies. In addition, the biocompatibility of hydrogels was evaluated in vivo by cytotoxicity and cell migration assays and the burn healing ability of hydrogels was tested in vivo using burn-induced wounds in mice.
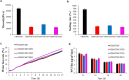
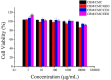
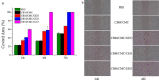
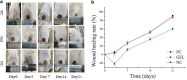
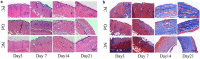
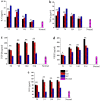
Results: The different essential oils exhibited different mixing abilities with the hydrogel matrix (CMC and CBM), which caused varying levels of reduction in essential oil hydrogel viscosity, swelling and water vapor transmission. Among the developed hydrogels, the CBM/CMC/EEO hydrogel exhibited optimal antibacterial activities of 46.26 ± 2.22% and 63.05 ± 0.99% against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, respectively, along with cell viability (>92.37%) and migration activity. Furthermore, the CBM/CMC/EEO hydrogel accelerated wound healing in mouse burn models by promoting the recovery of dermis and epidermis as observed using a hematoxylin-eosin and Masson's trichrome staining assay. The findings from an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay demonstrated that the CBM/CMC/EEO hydrogel could repair wounds through interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α downregulation and transforming growth factor-β, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and epidermal growth factor upregulation.
Conclusions: This study successfully prepared a porous CBM/CMC/EEO hydrogel with high antibacterial activity, favorable swelling, optimal rheological properties, superior water retention and water vapor transmission performance and a significant effect on skin repair in vitro and in vivo. The results indicate that the CBM/CMC/EEO hydrogel has the potential for use as a promising burn dressing material for skin burn repair.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Burn; Carboxymethyl chitosan; Eucalyptus essential oil; Hydrogel; Wound healing.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential Oil Nanoemulsion Hydrogel with Anti-Biofilm Activity for the Treatment of Infected Wounds.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Mar 9;15(6):1376. doi: 10.3390/polym15061376. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36987156 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin, silver titanate, Bletilla striata polysaccharide and carboxymethyl chitosan in a porous sponge dressing for burn wound healing.J Integr Med. 2023 Sep;21(5):487-495. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2023.07.002. Epub 2023 Jul 25. J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 37544834
-
[Effects of methacrylic anhydride gelatin hydrogel loaded with silver and recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor on deep partial-thickness burn wounds in rabbits].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 Jul 20;38(7):640-649. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20210726-00260. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35899331 Chinese.
-
How the combination of alginate and chitosan can fabricate a hydrogel with favorable properties for wound healing.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 3;10(11):e32040. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32040. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38912439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Role of Natural Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Wound Dressings in Biomedical Applications.Gels. 2022 Oct 12;8(10):646. doi: 10.3390/gels8100646. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36286147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polymer-Based Wound Dressings Loaded with Essential Oil for the Treatment of Wounds: A Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 5;17(7):897. doi: 10.3390/ph17070897. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amphiphilic Chitosan Porous Membranes as Potential Therapeutic Systems with Analgesic Effect for Burn Care.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Oct 5;12(10):973. doi: 10.3390/membranes12100973. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295732 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Extracts as Skin Care and Therapeutic Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 22;24(20):15444. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015444. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Luminol-conjugated cyclodextrin biological nanoparticles for the treatment of severe burn-induced intestinal barrier disruption.Burns Trauma. 2024 Mar 3;12:tkad054. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkad054. eCollection 2024. Burns Trauma. 2024. PMID: 38444636 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Therapeutic Effects of Essential Oils on the Oral Microbiome.Pharmacy (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;11(1):33. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy11010033. Pharmacy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36827671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Loo Y, Wong YC, Cai EZ, Ang CH, Raju A, Lakshmanan A, et al. . Ultrashort peptide nanofibrous hydrogels for the acceleration of healing of burn wounds. Biomaterials. 2014;35:4805–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

