Sleep problems in rheumatoid arthritis over 12 years from diagnosis: results from the Swedish EIRA study
- PMID: 34987091
- PMCID: PMC8734013
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001800
Sleep problems in rheumatoid arthritis over 12 years from diagnosis: results from the Swedish EIRA study
Abstract
Objective: Most studies of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and sleep have focused on established RA. We here investigate sleep quality and sleep duration in patients with newly diagnosed RA and during 1-12 years after diagnosis.
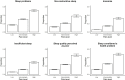
Methods: Data were collected on sleep 1-12 years after diagnosis from patients diagnosed 1998-2018 in the Swedish study Epidemiological Investigation of RA. Six sleep domains (sleep problems, non-restorative sleep, insomnia, insufficient sleep, sleep quality perceived as poor and sleep considered a health problem); a global sleep score and time spent in bed were estimated. Using logistic regression, ORs were calculated for each sleep outcome by disease duration. We explored whether pain (low (Visual Analogue Scale=0-20 mm, reference), intermediate=21-70, high=71-100) or functional impairment (Health Assessment Questionnaire>1.0) was associated with problems.
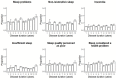
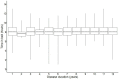
Results: We had sleep data on 4131 observations (n=3265 individuals). Problems with ≥1 sleep domain (global sleep score) was reported in 1578 observations (38%) and increased with disease duration (OR 1.04, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.07). Median time in bed was 8 hours (Q1-Q3: 7.5-9.0). High-grade pain increased the likelihood of sleep problems ~3-9 fold, and increased functional impairment ~4-8 fold.
Conclusion: In this cohort of newly diagnosed patients with RA with access to the current treatment from diagnosis, we did not find any major problems with sleep, and existing sleep problems related mainly to pain and reduced function. Treatment of sleep problems in RA should be guided towards treating the underlying problem causing the sleep disturbance.
Keywords: epidemiology; patient reported outcome measures; rheumatoid arthritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sleep disturbance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is related to fatigue, disease activity, and other patient-reported outcomes.Scand J Rheumatol. 2017 Mar;46(2):95-103. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2016.1168482. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27319613
-
Sleep quality and functional disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Sleep Med. 2011 Feb 15;7(1):49-55. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011. PMID: 21344040 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep Disorders Among Individuals With Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2023 Jun;75(6):1250-1260. doi: 10.1002/acr.24999. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 35997482
-
Sleep impairment: an obstacle to achieve optimal quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Dec;38(12):2183-2192. doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4155-5. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 30206671 Review.
-
Heat of the night: sleep disturbance activates inflammatory mechanisms and induces pain in rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023 Sep;19(9):545-559. doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00997-3. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37488298 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing sleep-related breathing disorders among newly diagnosed rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis patients: a cross-sectional study.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Jun;44(6):1025-1034. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05610-8. Epub 2024 May 7. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38713410 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Poor Sleep Quality and Associated Factors in Individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Sep 8;59(9):1633. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091633. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37763752 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Sleep Traits and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 30;10:940161. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940161. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35844889 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Clock Genes in Maintaining Circadian Rhythm and Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathophysiology.Cureus. 2023 May 16;15(5):e39104. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39104. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37378201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease activity and disease-related factors are drivers of patient global assessment in rheumatoid arthritis: a real-life cross-sectional study.Rheumatol Int. 2023 Oct;43(10):1885-1895. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05383-6. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Rheumatol Int. 2023. PMID: 37454308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
