Drug delivery systems for RNA therapeutics
- PMID: 34983972
- PMCID: PMC8724758
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-021-00439-4
Drug delivery systems for RNA therapeutics
Abstract
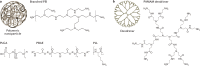
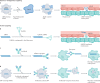
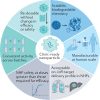
RNA-based gene therapy requires therapeutic RNA to function inside target cells without eliciting unwanted immune responses. RNA can be ferried into cells using non-viral drug delivery systems, which circumvent the limitations of viral delivery vectors. Here, we review the growing number of RNA therapeutic classes, their molecular mechanisms of action, and the design considerations for their respective delivery platforms. We describe polymer-based, lipid-based, and conjugate-based drug delivery systems, differentiating between those that passively and those that actively target specific cell types. Finally, we describe the path from preclinical drug delivery research to clinical approval, highlighting opportunities to improve the efficiency with which new drug delivery systems are discovered.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
J.E.D. is a consultant for GV. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional nanostructures for effective delivery of small interfering RNA therapeutics.Theranostics. 2014 Sep 19;4(12):1211-32. doi: 10.7150/thno.8491. eCollection 2014. Theranostics. 2014. PMID: 25285170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Transport Systems and Clinical Applications for Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Drugs.Mol Diagn Ther. 2018 Oct;22(5):551-569. doi: 10.1007/s40291-018-0338-8. Mol Diagn Ther. 2018. PMID: 29926308 Review.
-
Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms for RNAi Therapeutics Targeting COVID-19 Disease in the Respiratory Tract.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 22;23(5):2408. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052408. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-based therapeutics in cardiovascular disease.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2020 May;35(3):191-198. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000724. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32068614 Review.
-
Toxicogenomics of cationic lipid-based vectors for gene therapy: impact of microarray technology.Curr Drug Deliv. 2005 Oct;2(4):429-41. doi: 10.2174/156720105774370249. Curr Drug Deliv. 2005. PMID: 16305446 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting miR-29 mitigates skeletal senescence and bolsters therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stromal cells.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Aug 20;5(8):101665. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101665. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39168101 Free PMC article.
-
TREAT: Therapeutic RNAs exploration inspired by artificial intelligence technology.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 8;20:5680-5689. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.011. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36320935 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-targeted delivery of lnc antisense RNA against RCAS1 by live-attenuated tryptophan-auxotrophic Salmonella inhibited 4T1 breast tumors and metastasis in mice.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Oct 13;34:102053. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102053. eCollection 2023 Dec 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37941832 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Genetic Therapies: Balancing Risk and Benefit in Patients with Heart Failure.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024 Sep;26(9):973-983. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02096-5. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39110386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Durable protective efficiency provide by mRNA vaccines require robust immune memory to antigens and weak immune memory to lipid nanoparticles.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Feb 9;25:100988. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100988. eCollection 2024 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38379935 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

