A Brief Overview of lncRNAs in Endothelial Dysfunction-Associated Diseases: From Discovery to Characterization
- PMID: 34968230
- PMCID: PMC8594677
- DOI: 10.3390/epigenomes3030020
A Brief Overview of lncRNAs in Endothelial Dysfunction-Associated Diseases: From Discovery to Characterization
Abstract
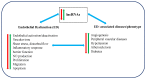
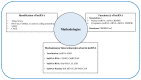
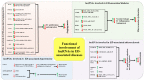
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a novel class of regulatory RNA molecules and they are involved in many biological processes and disease developments. Several unique features of lncRNAs have been identified, such as tissue-and/or cell-specific expression pattern, which suggest that they could be potential candidates for therapeutic and diagnostic applications. More recently, the scope of lncRNA studies has been extended to endothelial biology research. Many of lncRNAs were found to be critically involved in the regulation of endothelial function and its associated disease progression. An improved understanding of endothelial biology can thus facilitate the discovery of novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for endothelial dysfunction-associated diseases, such as abnormal angiogenesis, hypertension, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanism of lncRNA remains undefined in previous published studies. Therefore, in this review, we aimed to discuss the current methodologies for discovering and investigating the functions of lncRNAs and, in particular, to address the functions of selected lncRNAs in endothelial dysfunction-associated diseases.
Keywords: angiogenesis; atherosclerosis; diabetes; endothelial dysfunction; hypertension; lncRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNAs and circular RNAs as endothelial cell messengers in hypertension: mechanism insights and therapeutic potential.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jul;47(7):5535-5547. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05601-5. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32567025 Review.
-
Endothelial dysfunction and cardiometabolic diseases: Role of long non-coding RNAs.Life Sci. 2016 Dec 15;167:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27838210 Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis identified a novel 3-LncRNA regulatory network of transthyretin attenuating glucose induced hRECs dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Oct 15;12(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0596-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31615521 Free PMC article.
-
Conceptual approaches for lncRNA drug discovery and future strategies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2012 Jun;7(6):503-13. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2012.682055. Epub 2012 May 5. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22559214 Review.
-
RNA-seq identifies long non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets for human corneal endothelial dysfunction under oxidative stress.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Dec;213:108820. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108820. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34728181
Cited by
-
Role of long noncoding RNAs in diabetes-associated peripheral arterial disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jul 24;23(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02327-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39049097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome editing technologies: CRISPR, LEAPER, RESTORE, ARCUT, SATI, and RESCUE.EXCLI J. 2021 Jan 4;20:19-45. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-3070. eCollection 2021. EXCLI J. 2021. PMID: 33510590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

