Cat allergen exposure in a naturalistic exposure chamber: A prospective observational study in cat-allergic subjects
- PMID: 34962661
- PMCID: PMC9303194
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.14087
Cat allergen exposure in a naturalistic exposure chamber: A prospective observational study in cat-allergic subjects
Abstract
Background: To determine the proportion and reproducibility of cat-allergic mild asthmatics with early asthmatic response (EAR) during cat allergen exposure in a naturalistic exposure chamber (NEC).
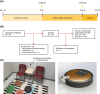
Methods: This was a prospective, observational study in 30 cat-allergic mild asthmatics who received two 180-min cat-allergen (Felis domesticus allergen 1 [Fel d 1]) challenges 27 days apart in an NEC.
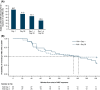
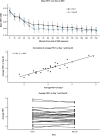
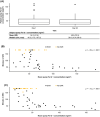
Results: An EAR (≥20% reduction from baseline in forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1]) was observed in 67% and 52% of subjects at first and second NEC exposure, respectively, with similar median time to EAR; 44% of subjects had an EAR on days 1 and 28. Late asthmatic response (≥15% reduction in FEV1 within 24 h of NEC exit) was observed in 33% of subjects following either exposure. Average FEV1 and total nasal symptom score during NEC exposure were highly correlated within subjects between NEC exposures (r = 0.91, p < 0.0001; r = 0.73, p < 0.001), but total ocular symptom score was not. Time to EAR, but not average FEV1, was significantly associated with NEC Fel d 1 concentration, which was variable. There were no serious adverse events; 12/30 subjects experienced 20 adverse events (including asthma, 10%; headache, 10%).
Conclusions: The NEC model demonstrates that average FEV1 change is highly reproducible and has a low correlation with cat allergen levels. However, time to EAR and incidence of EAR are less reproducible and are highly correlated with NEC allergen levels. Average FEV1, rather than incidence of EAR or time to EAR, could be considered as an endpoint for interventional trials testing cat-specific anti-allergy therapies using an NEC.
Keywords: allergy treatment; asthma; challenge tests.
© 2022 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Clinical & Experimental Allergy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
REGN1908/1909 prevented cat allergen-induced early asthmatic responses in an environmental exposure unit.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Dec;150(6):1437-1446. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.06.025. Epub 2022 Aug 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35934082 Clinical Trial.
-
Rhinoconjunctivitis severity induced by cat exposure influences early and late asthmatic responses: Evidence from an environmental exposure chamber.Clin Exp Allergy. 2024 Aug;54(8):596-606. doi: 10.1111/cea.14485. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Clin Exp Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38660824
-
Effect of exposure to low levels of ozone on the response to inhaled allergen in allergic asthmatic patients.Chest. 1998 Sep;114(3):752-6. doi: 10.1378/chest.114.3.752. Chest. 1998. PMID: 9743162 Clinical Trial.
-
Allergen-induced early and late asthmatic responses to inhaled seasonal and perennial allergens.Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Nov;45(11):1647-53. doi: 10.1111/cea.12587. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015. PMID: 26115509
-
Study of Cat Allergy Using Controlled Methodology-A Review of the Literature and a Call to Action.Front Allergy. 2022 Mar 17;3:828091. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.828091. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35386639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of Fel d 1 chain 2 genome-edited cats by CRISPR-Cas9 system.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;14(1):4987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55464-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38424152 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress and clinical application of allergen nasal provocation test].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Jun;37(6):415-422. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.06.003. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37253513 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Gronlund H, Saarne T, Gafvelin G, van Hage M. The major cat allergen, Fel d 1, in diagnosis and therapy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;151(4):265‐274. - PubMed
-
- Kleine‐Tebbe J, Kleine‐Tebbe A, Jeep S, et al. Role of the major allergen (Fel d I) in patients sensitized to cat allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1993;100(3):256‐262. - PubMed
-
- Bollinger ME, Eggleston PA, Flanagan E, Wood RA. Cat antigen in homes with and without cats may induce allergic symptoms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;97(4):907‐914. - PubMed
-
- Bollinger ME, Wood RA, Chen P, Eggleston PA. Measurement of cat allergen levels in the home by use of an amplified ELISA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;101(1 Pt 1):124‐125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

