Sigma-1 Receptor is a Pharmacological Target to Promote Neuroprotection in the SOD1G93A ALS Mice
- PMID: 34955848
- PMCID: PMC8702863
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.780588
Sigma-1 Receptor is a Pharmacological Target to Promote Neuroprotection in the SOD1G93A ALS Mice
Abstract
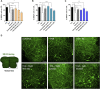
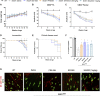
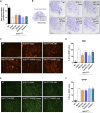
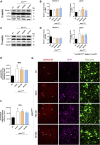
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the death of motoneurons (MNs) with a poor prognosis. There is no available cure, thus, novel therapeutic targets are urgently needed. Sigma-1 receptor (Sig-1R) has been reported as a target to treat experimental models of degenerative diseases and, importantly, mutations in the Sig-1R gene cause several types of motoneuron disease (MND). In this study we compared the potential therapeutic effect of three Sig-1R ligands, the agonists PRE-084 and SA4503 and the antagonist BD1063, in the SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS. Pharmacological administration was from 8 to 16 weeks of age, and the neuromuscular function and disease progression were evaluated using nerve conduction and rotarod tests. At the end of follow up (16 weeks), samples were harvested for histological and molecular analyses. The results showed that PRE-084, as well as BD1063 treatment was able to preserve neuromuscular function of the hindlimbs and increased the number of surviving MNs in the treated female SOD1G93A mice. SA4503 tended to improve motor function and preserved neuromuscular junctions (NMJ), but did not improve MN survival. Western blot analyses revealed that the autophagic flux and the endoplasmic reticulum stress, two pathways implicated in the physiopathology of ALS, were not modified with Sig-1R treatments in SOD1G93A mice. In conclusion, Sig-1R ligands are promising tools for ALS treatment, although more research is needed to ascertain their mechanisms of action.
Keywords: SOD1 G93A transgenic; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; motoneuron; neurodegenerative disease; sigma-1 receptor.
Copyright © 2021 Gaja-Capdevila, Hernández, Navarro and Herrando-Grabulosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EST79232 and EST79376, Two Novel Sigma-1 Receptor Ligands, Exert Neuroprotection on Models of Motoneuron Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6737. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126737. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743175 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma-1R agonist improves motor function and motoneuron survival in ALS mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2012 Oct;9(4):814-26. doi: 10.1007/s13311-012-0140-y. Neurotherapeutics. 2012. PMID: 22935988 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Role of Neuregulin 1 Type III in SOD1-Linked Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jul;17(3):1048-1060. doi: 10.1007/s13311-019-00811-7. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 31965551 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma-1 Receptor in Motoneuron Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:235-254. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315275 Review.
-
Novel Therapeutic Target for Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Modulation of Neuroinflammation with Sig-1R Ligands.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 25;12(3):363. doi: 10.3390/biom12030363. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327555 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging diagnosis in peripheral nerve injury.Front Neurol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1250808. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1250808. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37780718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential roles of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Feb 15;15:1047897. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1047897. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36875699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Sigma-1 Receptor Ligands on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration.Cells. 2022 Mar 23;11(7):1083. doi: 10.3390/cells11071083. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406646 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of somatosensory neuron involvement in the SOD1G93A mouse model.Sci Rep. 2022 May 9;12(1):7600. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11767-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35534694 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring dysregulated miRNAs in ALS: implications for disease pathogenesis and early diagnosis.Neurol Sci. 2024 Nov 21. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07840-x. Online ahead of print. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39570437
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

