Constitutive, Basal, and β-Alanine-Mediated Activation of the Human Mas-Related G Protein-Coupled Receptor D Induces Release of the Inflammatory Cytokine IL-6 and Is Dependent on NF-κB Signaling
- PMID: 34948051
- PMCID: PMC8703779
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413254
Constitutive, Basal, and β-Alanine-Mediated Activation of the Human Mas-Related G Protein-Coupled Receptor D Induces Release of the Inflammatory Cytokine IL-6 and Is Dependent on NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
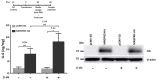
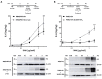
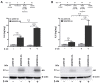
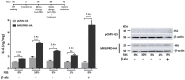
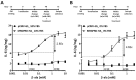
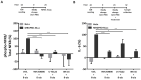
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have emerged as key players in regulating (patho)physiological processes, including inflammation. Members of the Mas-related G protein coupled receptors (MRGPRs), a subfamily of GPCRs, are largely expressed by sensory neurons and known to modulate itch and pain. Several members of MRGPRs are also expressed in mast cells, macrophages, and in cardiovascular tissue, linking them to pseudo-allergic drug reactions and suggesting a pivotal role in the cardiovascular system. However, involvement of the human Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor D (MRGPRD) in the regulation of the inflammatory mediator interleukin 6 (IL-6) has not been demonstrated to date. By stimulating human MRGPRD-expressing HeLa cells with the agonist β-alanine, we observed a release of IL-6. β-alanine-induced signaling through MRGPRD was investigated further by probing downstream signaling effectors along the Gαq/Phospholipase C (PLC) pathway, which results in an IkB kinases (IKK)-mediated canonical activation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and stimulation of IL-6 release. This IL-6 release could be blocked by a Gαq inhibitor (YM-254890), an IKK complex inhibitor (IKK-16), and partly by a PLC inhibitor (U-73122). Additionally, we investigated the constitutive (ligand-independent) and basal activity of MRGPRD and concluded that the observed basal activity of MRGPRD is dependent on the presence of fetal bovine serum (FBS) in the culture medium. Consequently, the dynamic range for IL-6 detection as an assay for β-alanine-mediated activation of MRGPRD is substantially increased by culturing the cells in FBS free medium before treatment. Overall, the observation that MRGPRD mediates the release of IL-6 in an in vitro system, hints at a role as an inflammatory mediator and supports the notion that IL-6 can be used as a marker for MRGPRD activation in an in vitro drug screening assay.
Keywords: GPCR; Gq inhibitor; MRGPRD; NF-kB; constitutive receptor; interleukin 6; β-alanine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in (a) the design of the study, (b) in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, (c) in the writing of the manuscript, or (d) in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor D participates in inflammatory pain by promoting NF-κB activation through interaction with TAK1 and IKK complex.Cell Signal. 2020 Dec;76:109813. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109813. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 33080316
-
Facilitation of MrgprD by TRP-A1 promotes neuropathic pain.FASEB J. 2019 Jan;33(1):1360-1373. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800615RR. Epub 2018 Aug 27. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30148678 Free PMC article.
-
Nonpeptidergic neurons suppress mast cells via glutamate to maintain skin homeostasis.Cell. 2021 Apr 15;184(8):2151-2166.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.002. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Cell. 2021. PMID: 33765440 Free PMC article.
-
Reprint of Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Dec;17(4):1185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24263067 Review.
-
Mas-related G protein-coupled receptors (Mrgprs) - Key regulators of neuroimmune interactions.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Apr 1;749:135724. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135724. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33600909 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure, function, and pharmacology of MRGPRs.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Apr;44(4):237-251. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36870785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Methylation Negatively Regulates Gene Expression of Key Cytokines Secreted by BMMCs Recognizing FMDV-VLPs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10849. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910849. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409178 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of Alamandine Receptor MrgD in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Is Associated with a Worse Prognosis and Unfavorable Response to Antiangiogenic Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1499. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031499. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338778 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into the activation mechanism of MrgD with heterotrimeric Gi-protein revealed by cryo-EM.Commun Biol. 2022 Jul 15;5(1):707. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03668-3. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35840655 Free PMC article.
-
Role of signal transduction pathways in IL-1β-induced apoptosis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Jan;11(1):e762. doi: 10.1002/iid3.762. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 36705417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avula L.R., Buckinx R., Favoreel H., Cox E., Adriaensen D., van Nassauw L., Timmermans J.P. Expression and distribution patterns of Mas-related gene receptor subtypes A-H in the mouse intestine: Inflammation-induced changes. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013;139:639–658. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1086-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

