Micro/Nanopatterned Superhydrophobic Surfaces Fabrication for Biomolecules and Biomaterials Manipulation and Analysis
- PMID: 34945349
- PMCID: PMC8708205
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12121501
Micro/Nanopatterned Superhydrophobic Surfaces Fabrication for Biomolecules and Biomaterials Manipulation and Analysis
Abstract
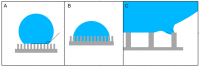
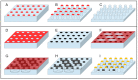
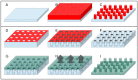
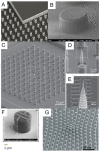
Superhydrophobic surfaces display an extraordinary repulsion to water and water-based solutions. This effect emerges from the interplay of intrinsic hydrophobicity of the surface and its morphology. These surfaces have been established for a long time and have been studied for decades. The increasing interest in recent years has been focused towards applications in many different fields and, in particular, biomedical applications. In this paper, we review the progress achieved in the last years in the fabrication of regularly patterned superhydrophobic surfaces in many different materials and their exploitation for the manipulation and characterization of biomaterial, with particular emphasis on the issues affecting the yields of the fabrication processes and the quality of the manufactured devices.
Keywords: biomolecules; micro/nanofabrication; superhydrophobic surfaces.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Droplet manipulation on superhydrophobic surfaces based on external stimulation: A review.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Aug;306:102724. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102724. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 35780752 Review.
-
Fabrication of Transferable and Micro/Nanostructured Superhydrophobic Surfaces Using Demolding and iCVD Processes.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023 Jan 11;15(1):2368-2375. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c17613. Epub 2022 Dec 27. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 36574499
-
Advances in Bioinspired Superhydrophobic Surfaces Made from Silicones: Fabrication and Application.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;15(3):543. doi: 10.3390/polym15030543. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro/nano-structured superhydrophobic surfaces in the biomedical field: part II: applications overview.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015 Jan;10(2):271-97. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.175. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25600971 Review.
-
Design and fabrication of micro-textures for inducing a superhydrophobic behavior on hydrophilic materials.Langmuir. 2007 Apr 10;23(8):4310-4. doi: 10.1021/la063572r. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Langmuir. 2007. PMID: 17371061
Cited by
-
Wall-free droplet microfluidics for probing biological processes by high-brilliance X-ray scattering techniques.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Nov 16;9:1049327. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1049327. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36465565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Properties of Polyimide/Polysulfonamide/Polyethylene Glycol (PI/PSA/PEG) Hydrophobic Nanofibrous Membranes.Materials (Basel). 2024 Aug 21;17(16):4135. doi: 10.3390/ma17164135. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39203312 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Scale Structure and Directional Hydrophobicity of Titanium Alloy Surface Using Electrical Discharge.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jun 12;13(6):937. doi: 10.3390/mi13060937. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35744551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koch K., Bhushan B., Barthlott W. Multifunctional surface structures of plants: An inspiration for biomimetics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009;54:137–178. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2008.07.003. - DOI
-
- Wong T.S., Sun T., Feng L., Aizenberg J. Interfacial materials with special wettability. MRS Bull. 2013;38:366–371. doi: 10.1557/mrs.2013.99. - DOI
-
- Blossey R., Scientifique C. 2003_Self-cleaning surfaces–virtual realities_Nature. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2003;2:301–306. - PubMed
-
- Ghasemlou M., Le P.H., Daver F., Murdoch B.J., Ivanova E.P., Adhikari B. Robust and Eco-Friendly Superhydrophobic Starch Nanohybrid Materials with Engineered Lotus Leaf Mimetic Multiscale Hierarchical Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2021;13:36558–36573. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c09959. - DOI - PubMed

