Omicron variant showed lower neutralizing sensitivity than other SARS-CoV-2 variants to immune sera elicited by vaccines after boost
- PMID: 34935594
- PMCID: PMC8788341
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2021.2022440
Omicron variant showed lower neutralizing sensitivity than other SARS-CoV-2 variants to immune sera elicited by vaccines after boost
Abstract
ABSTRACTThe emerging new VOC B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variant has raised serious concerns due to multiple mutations, reported significant immune escape, and unprecedented rapid spreading speed. Currently, studies describing the neutralization ability of different homologous and heterologous booster vaccination against Omicron are still lacking. In this study, we explored the immunogenicity of COVID-19 breakthrough patients, BBIBP-CorV homologous booster group and BBIBP-CorV/ZF2001 heterologous booster group against SARS-CoV-2 pseudotypes corresponding to the prototype, Beta, Delta, and the emergent Omicron variant.Notably, at 14 days post two-dose inactivated vaccines, pVNT titre increased to 67.4 GMTs against prototype, 8.85 against Beta and 35.07 against Delta, while neutralization activity against Omicron was below the lower limit of quantitation in 80% of the samples. At day 14 post BBIBP-CorV homologous booster vaccination, GMTs of pVNT significantly increased to 285.6, 215.7, 250.8, 48.73 against prototype, Beta, Delta, and Omicron, while at day 14 post ZF2001 heterologous booster vaccination, GMTs of pVNT significantly increased to 1436.00, 789.6, 1501.00, 95.86, respectively. Post booster vaccination, 100% samples showed positive neutralization activity against Omicron, albeit illustrated a significant reduction (5.86- to 14.98-fold) of pVNT against Omicron compared to prototype at 14 days after the homologous or heterologous vaccine boosters.Overall, our study demonstrates that vaccine-induced immune protection might more likely be escaped by Omicron compared to prototypes and other VOCs. After two doses of inactivated whole-virion vaccines as the "priming" shot, a third heterologous protein subunit vaccine and a homologous inactivated vaccine booster could improve neutralization against Omicron.
Keywords: Covid-19; Omicron; Pseudotyped viruses; neutralizing antibody; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by all the authors.
Figures
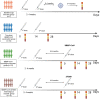


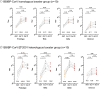
Similar articles
-
Homologous or heterologous booster of inactivated vaccine reduces SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant escape from neutralizing antibodies.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022 Dec;11(1):477-481. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2030200. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 35034583 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the mRNA vaccine CS-2034 as a heterologous booster versus homologous booster with BBIBP-CorV in adults aged ≥18 years: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2b trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2023 Sep;23(9):1020-1030. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00199-8. Epub 2023 May 19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37216958 Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of NVSI-06-07 as a heterologous booster after priming with BBIBP-CorV: a phase 2 trial.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jun 6;7(1):172. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00984-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35665745 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, immunogenicity, and protective effective of inhaled COVID-19 vaccines: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2024 Apr;96(4):e29625. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29625. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 38650361 Review.
-
A review of the immunogenicity and safety of booster doses of omicron variant-containing mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccines in adults and children.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2024 Jan-Dec;23(1):862-878. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2024.2397026. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 39234779 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of the conserved epitope peptide of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein as the broad-spectrum COVID-19 vaccine.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 16;108(1):486. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13331-y. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39412657 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Th1 versus Th2 immune bias on viral, pathological, and immunological dynamics in SARS-CoV-2 variant-infected human ACE2 knock-in mice.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105361. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105361. Epub 2024 Sep 30. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39353281 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2-associated hospitalization using sentinel surveillance in South Africa.Int J Epidemiol. 2024 Aug 14;53(5):dyae116. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyae116. Int J Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 39305220 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and pathogen features of COVID-19-associated infections during an Omicron strain outbreak in Guangzhou, China.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0340623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03406-23. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39240085 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential Immunization with Vaccines Based on SARS-CoV-2 Virus-like Particles Induces Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 19;12(8):927. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12080927. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nie J, Li Q, Wu J, et al. . Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by a pseudotyped virus-based assay. Nat Protoc. 2020 Nov;15(11):3699–3715. - PubMed
-
- Cele S, Jackson L, Khan K, et al. . SARS-CoV-2 Omicron has extensive but incomplete escape of Pfizer BNT162b2 elicited neutralization and requires ACE2 for infection. medRxiv. 2021.
-
- Wilhelm A, Widera M, Grikscheit K, et al. . Reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant by vaccine sera and monoclonal antibodies. medRxiv. 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

