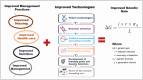
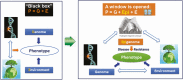
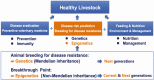
Consequence of epigenetic processes on animal health and productivity: is additional level of regulation of relevance?
- PMID: 34934525
- PMCID: PMC8683131
- DOI: 10.1093/af/vfab057
Consequence of epigenetic processes on animal health and productivity: is additional level of regulation of relevance?
Keywords: disease resistance; epigenetic factors; farm animals; livestock; production traits; transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impacts of Epigenetic Processes on the Health and Productivity of Livestock.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 23;11:613636. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.613636. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33708235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and transgenerational inheritance in domesticated farm animals.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2014 Oct 23;5(1):48. doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-5-48. eCollection 2014. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25810901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental epigenetics and epigenetic inheritance in domestic farm animals.Anim Reprod Sci. 2020 Sep;220:106316. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2020.106316. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Anim Reprod Sci. 2020. PMID: 32094003 Review.
-
Transgenerational transmission of environmental effects in livestock in the age of global warming.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Sep;28(5):445-454. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01325-0. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 36715961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenerational inheritance: how impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):518-540. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz017. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31374565
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide DNA Methylation and Transcriptome Integration Associates DNA Methylation Changes with Bovine Subclinical Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus chromogenes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 20;24(12):10369. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210369. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373515 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome DNA Methylation Variations in Mammary Gland Tissues from Holstein Cattle Producing Milk with Various Fat and Protein Contents.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 28;12(11):1727. doi: 10.3390/genes12111727. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828333 Free PMC article.
-
Improving hydrocarbon toxicity tolerance in poultry: role of genes and antioxidants.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 14;14:1060138. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1060138. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37388938 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation haplotype block signatures responding to Staphylococcus aureus subclinical mastitis and association with production and health traits.BMC Biol. 2024 Mar 14;22(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01843-y. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 38486242 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the genetic and epigenetic landscape governing intramuscular fat deposition in rabbits: Insights and implications.Food Chem (Oxf). 2024 Aug 30;9:100222. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2024.100222. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39290671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abobaker, H., Hu Y., Omer N.A., Hou Z., Idriss A.A., and Zhao R.. . 2019. Maternal betaine suppresses adrenal expression of cholesterol trafficking genes and decreases plasma corticosterone concentration in offspring pullets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 10:87. doi:10.1186/s40104-019-0396-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alharthi, A.S., Coleman D.N., Liang Y., Batistel F., Elolimy A.A., Yambao R.C., Abdel-Hamied E., Pan Y.X., Parys C., Alhidary I.A., . et al. 2019. Hepatic 1-carbon metabolism enzyme activity, intermediate metabolites, and growth in neonatal Holstein dairy calves are altered by maternal supply of methionine during late pregnancy. J. Dairy Sci. 102:10291–10303. doi:10.3168/jds.2019-16562. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chanthavixay, G., Kern C., Wang Y., Saelao P., Lamont S.J., Gallardo R.A., Rincon G., and Zhou H.. . 2020. Integrated transcriptome and histone modification analysis reveals NDV infection under heat stress affects bursa development and proliferation in susceptible chicken line. Front. Genet. 11:1176. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.567812. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
