VLDLR and ApoER2 are receptors for multiple alphaviruses
- PMID: 34929721
- PMCID: PMC8808280
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04326-0
VLDLR and ApoER2 are receptors for multiple alphaviruses
Abstract
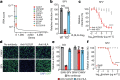
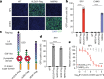
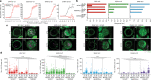
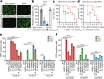
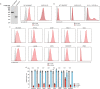
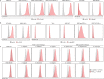
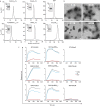
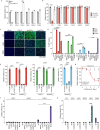
Alphaviruses, like many other arthropod-borne viruses, infect vertebrate species and insect vectors separated by hundreds of millions of years of evolutionary history. Entry into evolutionarily divergent host cells can be accomplished by recognition of different cellular receptors in different species, or by binding to receptors that are highly conserved across species. Although multiple alphavirus receptors have been described1-3, most are not shared among vertebrate and invertebrate hosts. Here we identify the very low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) as a receptor for the prototypic alphavirus Semliki forest virus. We show that the E2 and E1 glycoproteins (E2-E1) of Semliki forest virus, eastern equine encephalitis virus and Sindbis virus interact with the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of VLDLR and apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (ApoER2), two closely related receptors. Ectopic expression of either protein facilitates cellular attachment, and internalization of virus-like particles, a VLDLR LBD-Fc fusion protein or a ligand-binding antagonist block Semliki forest virus E2-E1-mediated infection of human and mouse neurons in culture. The administration of a VLDLR LBD-Fc fusion protein has protective activity against rapidly fatal Semliki forest virus infection in mouse neonates. We further show that invertebrate receptor orthologues from mosquitoes and worms can serve as functional alphavirus receptors. We propose that the ability of some alphaviruses to infect a wide range of hosts is a result of their engagement of evolutionarily conserved lipoprotein receptors and contributes to their pathogenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Identification of human and mosquito receptors for alphaviruses.Nature. 2022 Feb;602(7897):388-390. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-00052-3. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35046583 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for VLDLR recognition by eastern equine encephalitis virus.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 2;15(1):6548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50887-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39095394 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Semliki Forest virus in complex with its receptor VLDLR.Cell. 2023 May 11;186(10):2208-2218.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.032. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37098345
-
Structural basis for VLDLR recognition by eastern equine encephalitis virus.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 14:2023.11.14.567065. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.14.567065. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 2;15(1):6548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50887-9. PMID: 38014066 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A structural and functional perspective of alphavirus replication and assembly.Future Microbiol. 2009 Sep;4(7):837-56. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.59. Future Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19722838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mosquito-borne viruses in western Europe: a review.J Vector Ecol. 1999 Jun;24(1):1-39. J Vector Ecol. 1999. PMID: 10436876 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of O'nyong-nyong virus: A less studied Togaviridae with pandemic potential.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2355201. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2355201. Epub 2024 May 26. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38797948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus - animal virology, immunology, and pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1194386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1194386. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153562 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Oncolytic Activity of Sindbis Virus with the Help of GM-CSF in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 29;25(13):7195. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137195. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000311 Free PMC article.
-
Residues L55 and W69 of Tva Mediate Entry of Subgroup A Avian Leukosis Virus.J Virol. 2022 Sep 28;96(18):e0067822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00678-22. Epub 2022 Sep 7. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36069550 Free PMC article.
-
LDLR is an entry receptor for Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus.Cell Res. 2024 Feb;34(2):140-150. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00917-w. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38182887 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

