Plant protein reduces serum cholesterol levels in hypercholesterolemia hamsters by modulating the compositions of gut microbiota and metabolites
- PMID: 34927019
- PMCID: PMC8649741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103435
Plant protein reduces serum cholesterol levels in hypercholesterolemia hamsters by modulating the compositions of gut microbiota and metabolites
Abstract
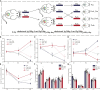
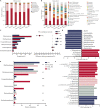
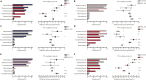
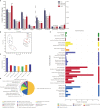
Plant proteins exert effects of reducing cardio-cerebrovascular disease-related mortality partly via cholesterol-lowering, which was associated with gut microbiota. Here, we verify that there are significant differences in cholesterol levels among hamsters consuming different proteins. The decisive roles of gut microbiota in regulating host cholesterol are illustrated by the fact that the difference in serum cholesterol levels between hamsters feeding with pea protein and pork protein disappeared when treated with antibiotics. The results of cross-over intervention of pea and pork protein show that serum cholesterol levels are reversed with dietary exchange. The corresponding changes in microbiota suggest that Muribaculaceae are responsible for the inhibitory effect of pea protein on serum cholesterol level, whereas the opposite effect of pork protein is due to Erysipelotrichaceae. Moreover, pea protein supplement alters cecal metabolites including arginine/histidine pathway, primary bile acid biosynthesis, short-chain fatty acids, and other lipid-like molecules involved in cholesterol metabolism.
Keywords: Biological science; Endocrinology; Microbiology.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oryzanol alleviates high fat and cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia associated with the modulation of the gut microbiota in hamsters.Food Funct. 2022 Apr 20;13(8):4486-4501. doi: 10.1039/d1fo03464b. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 35348138
-
Effect of Oat and Tartary Buckwheat - Based Food on Cholesterol - Lowering and Gut Microbiota in Hypercholesterolemic Hamsters.J Oleo Sci. 2019 Mar 1;68(3):251-259. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess18221. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Oleo Sci. 2019. PMID: 30760672
-
Dietary cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites.Gut. 2021 Apr;70(4):761-774. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319664. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Gut. 2021. PMID: 32694178 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Gut Microbiota on Cholesterol Metabolism in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8074. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158074. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Oats and Oat Beta Glucan: Modes of Action and Potential Role of Bile Acids and the Microbiome.Front Nutr. 2019 Nov 27;6:171. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00171. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31828074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pea Albumin Extracted from Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seeds Ameliorates High-Fat-Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipogenesis and Lipolysis Pathways.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2232. doi: 10.3390/nu16142232. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064674 Free PMC article.
-
Totum-070, a Polyphenol-Rich Plant Extract, Prevents Hypercholesterolemia in High-Fat Diet-Fed Hamsters by Inhibiting Intestinal Cholesterol Absorption.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 9;15(24):5056. doi: 10.3390/nu15245056. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38140315 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Bioactive Compound Effects from Primary Legume Protein Sources in Human and Animal Health.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 May 1;46(5):4203-4233. doi: 10.3390/cimb46050257. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38785525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Analysis of Gut Microbiome and Lipid Metabolism in Mice Infected with Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae.Metabolites. 2022 Sep 22;12(10):892. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100892. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36295794 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted Microbiota of Colon Results in Worse Immunity and Metabolism in Low-Birth-Weight Jinhua Newborn Piglets.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 4;12(7):1371. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071371. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abboud K.Y., Reis S.K., Martelli M.E., Zordão O.P., Tannihão F., de Souza A.Z.Z., Assalin H.B., Guadagnini D., Rocha G.Z., Saad M.J.A., Prada P.O. Oral glutamine supplementation reduces obesity, pro-inflammatory markers, and improves insulin sensitivity in DIO wistar rats and reduces waist circumference in overweight and obese humans. Nutrients. 2019;11:536. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abeysekara S., Chilibeck P.D., Vatanparast H., Zello G.A. A pulse-based diet is effective for reducing total and LDL-cholesterol in older adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2012;108:S103–S110. - PubMed
-
- Augé N., Maupas-Schwalm F., Elbaz M., Thiers J.C., Waysbort A., Itohara S., Krell H.W., Salvayre R., Nègre-Salvayre A. Role for matrix metalloproteinase-2 in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced activation of the sphingomyelin/ceramide pathway and smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation. 2004;110:571–578. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

