Topical Treatment of Human Skin and Cultured Keratinocytes with High-Dose Spironolactone Reduces XPB Expression and Induces Toxicity
- PMID: 34909723
- PMCID: PMC8659383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100023
Topical Treatment of Human Skin and Cultured Keratinocytes with High-Dose Spironolactone Reduces XPB Expression and Induces Toxicity
Abstract
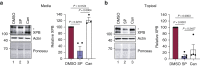
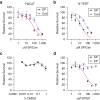
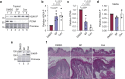
Spironolactone (SP) is used to treat a variety of disparate disease states ranging from heart failure to acne through antagonism of the mineralocorticoid and androgen receptors. Although normally taken as an oral medication, recent studies have explored the topical application of SP onto the skin. However, because SP induces the proteolytic degradation of the XPB protein, which plays critical roles in DNA repair and transcription, there may be safety concerns with the use of topical SP. In this study, we show that the topical application of a high concentration of either SP or its metabolite canrenone onto human skin ex vivo lowers XPB protein levels and induces toxic responses in the epidermis. Interestingly, although SP and canrenone both inhibit cell proliferation, induce replication stress responses, and stimulate apoptotic signaling at high concentrations in cultured keratinocytes in vitro, these effects were not correlated with XPB protein loss. Thus, high concentrations of SP and canrenone likely inhibit cell proliferation and induce toxicity through additional mechanisms to XPB proteolytic degradation. This work suggests that care may need to be taken when using high concentrations of SP directly on human skin.
Keywords: Can, canrenone; KC, keratinocyte; MR, mineralocorticoid receptor; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; SP, spironolactone.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spironolactone Depletes the XPB Protein and Inhibits DNA Damage Responses in UVB-Irradiated Human Skin.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 Feb;139(2):448-454. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.07.039. Epub 2018 Sep 15. J Invest Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30227140 Free PMC article.
-
Spironolactone and XPB: An Old Drug with a New Molecular Target.Biomolecules. 2020 May 13;10(5):756. doi: 10.3390/biom10050756. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32414008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific Inhibition of HIV Infection by the Action of Spironolactone in T Cells.J Virol. 2016 Nov 14;90(23):10972-10980. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01722-16. Print 2016 Dec 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27681137 Free PMC article.
-
The XPB Subunit of the TFIIH Complex Plays a Critical Role in HIV-1 Transcription and XPB Inhibition by Spironolactone Prevents HIV-1 Reactivation from Latency.J Virol. 2021 Feb 15;95(4):e01247-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01247-20. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33239456 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolism and biopharmaceutics of spironolactone in man.Rev Drug Metab Drug Interact. 1987;5(4):273-302. doi: 10.1515/dmdi.1987.5.4.273. Rev Drug Metab Drug Interact. 1987. PMID: 3333882 Review.
Cited by
-
Forging a Functional Cure for HIV: Transcription Regulators and Inhibitors.Viruses. 2022 Sep 7;14(9):1980. doi: 10.3390/v14091980. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Raouf H., Aly U.F., Medhat W., Ahmed S.S., Abdel-Aziz R.T.A. A novel topical combination of minoxidil and spironolactone for androgenetic alopecia: clinical, histopathological, and physicochemical study. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14678. - PubMed
-
- Alekseev S., Ayadi M., Brino L., Egly J.M., Larsen A.K., Coin F. A small molecule screen identifies an inhibitor of DNA repair inducing the degradation of TFIIH and the chemosensitization of tumor cells to platinum. Chem Biol. 2014;21:398–407. - PubMed
-
- Arai K., Homma T., Morikawa Y., Ubukata N., Tsuruoka H., Aoki K., et al. Pharmacological profile of CS-3150, a novel, highly potent and selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;761:226–234. - PubMed
-
- Biggar R.J., Andersen E.W., Wohlfahrt J., Melbye M. Spironolactone use and the risk of breast and gynecologic cancers. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013;37:870–875. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

