Exploration of the Key Proteins of High-Grade Intraepithelial Neoplasia to Adenocarcinoma Sequence Using In-Depth Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
- PMID: 34880916
- PMCID: PMC8648452
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5538756
Exploration of the Key Proteins of High-Grade Intraepithelial Neoplasia to Adenocarcinoma Sequence Using In-Depth Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we aimed to provide a comprehensive description of typical features and identify key proteins associated with the high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia- (HIN-) adenocarcinoma (AC) sequence.
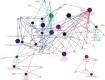
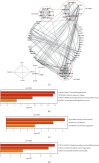
Methods: We conducted tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomic profiling of normal mucosa, HIN, and AC tissues. Protein clusters representative of the HIN-AC sequence were identified using heatmaps based on Pearson's correlation analysis. Gene ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Reactome analyses were performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) database, ClueGO plugin in Cytoscape, and the Metascape database. The prognostic value of the key proteins and their effects on the tumor microenvironment and consensus molecular subtype were explored based on The Cancer Genome Atlas.
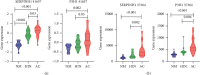
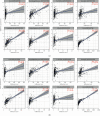
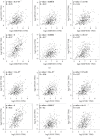
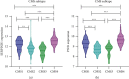
Results: We identified 536 proteins categorized into three clusters. Among the biological processes and pathways of the highly expressed proteins in the HIN-AC sequence, proteins were predominantly enriched in response to gut microbiota, cell proliferation, leukocyte migration, and extracellular matrix (ECM) organization events. SERPINH1 and P3H1 were identified as the key proteins that promote the HIN-AC sequence. In the correlation analysis of infiltrating immune cells, both SERPINH1 and P3H1 expression correlated negatively with tumor purity, while correlating positively with abundance of CD8+ T cells, B cells, macrophage/monocytes, dendritic cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, endothelial cells, neutrophils, and natural killer cells. Furthermore, both SERPINH1 and P3H1 expression positively correlated with common immune checkpoints and mesenchymal molecular subtype. High P3H1 expression was associated with poor disease-free survival and overall survival.
Conclusions: ECM-related biological processes and pathways are typical features of the HIN-AC sequence. SERPINH1 and P3H1 might be the key proteins in this sequence and be related to ECM remodeling and immune suppression status in CRC.
Copyright © 2021 Yin Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploration of the Key Proteins in the Normal-Adenoma-Carcinoma Sequence of Colorectal Cancer Evolution Using In-Depth Quantitative Proteomics.J Oncol. 2021 Jun 11;2021:5570058. doi: 10.1155/2021/5570058. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34194496 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes and pathways in scleral extracellular matrix remodeling in glaucoma: Potential therapeutic agents discovered using bioinformatics analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 4;18(7):1554-1565. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52846. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746571 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis of Expression and Prognostic Values of Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase short-chain in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Sep 7;18(16):3631-3643. doi: 10.7150/ijms.63953. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34790035 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the typical features of tubulovillous adenoma using in-depth quantitative proteomics analysis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):6831-6843. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1971036. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34585630 Free PMC article.
-
Identify potential prognostic indicators and tumor-infiltrating immune cells in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2022 Feb 25;42(2):BSR20212523. doi: 10.1042/BSR20212523. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35083488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of P3H family in cancer: implications for prognosis, tumor microenvironment and drug sensitivity.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 19;14:1374696. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1374696. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38706607 Free PMC article.
-
Basement membrane-related regulators for prediction of prognoses and responses to diverse therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Apr 20;16(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01504-z. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37081465 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of P3H1 as a Predictive Prognostic Biomarker for Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas Database.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023 Dec 1;16:1041-1053. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S437974. eCollection 2023. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38058295 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis of P3H1 and Experimental Validation in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;196(9):5974-5993. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04845-8. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38175417
References
-
- Wei X. B., Gao X. H., Wang H., et al. More advanced or aggressive colorectal cancer is associated with a higher incidence of “high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia” on biopsy-based pathological examination. Techniques in Coloproctology . 2012;16(4):277–283. doi: 10.1007/s10151-012-0827-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

