Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on haematocrit and haemoglobin levels and the associated cardiorenal benefits in T2DM patients: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 34878225
- PMCID: PMC8814934
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17115
Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on haematocrit and haemoglobin levels and the associated cardiorenal benefits in T2DM patients: A meta-analysis
Abstract
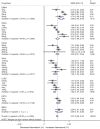
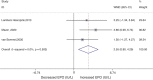
To explore the effect and magnitude of effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on haematocrit and haemoglobin and the related cardiorenal benefits in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), PubMed, Web of Science, CENTRAL and EMBASE were searched to identify eligible trials. Weighted mean differences (WMDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Seventy-eight studies were included in the meta-analysis. SGLT2 inhibitors significantly increased haematocrit and haemoglobin levels compared with control (total WMD 2.27% [95% CI 2.08, 2.47] and 6.20 g/L [95% CI 5.68, 6.73], respectively). Except for dapagliflozin (p = 0.000), no notable dose-dependent relationship was revealed for other SGLT2 inhibitors. The effect could be sustained or even slightly increased with long-term therapy (coef. =0.009, 95% CI [0.005, 0.013], p = 0.000). In subgroup analyses, haematocrit elevation increased with higher body mass index (BMI). A greater haematocrit elevation could be observed in white patients or when compared with active controls. In conclusion, SGLT2 inhibitors increased haematocrit and haemoglobin levels in T2DM patients. Changes in haematocrit and haemoglobin seem to be surrogate markers of improvement in renal metabolic stress, and important mediators involved in cardiorenal protection.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; cardiorenal protection; haematocrit; haemoglobin; meta-analysis; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there were no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of demographic characteristics and antihyperglycemic and cardiovascular drugs on the cardiorenal benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Nov 24;100(47):e27802. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027802. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34964748 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of sodium glucose co-transporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors on hematocrit levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jun;10(6):6467-6481. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1022. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34118855
-
Effect of sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors on sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 3;14:1203666. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1203666. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37465122 Free PMC article.
-
Competing Effects of Renin Angiotensin System Blockade and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Erythropoietin Secretion in Diabetes.Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(5):349-356. doi: 10.1159/000507272. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Am J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32241009 Review.
-
Comparison between SGLT2 inhibitors and DPP4 inhibitors added to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with indirect comparison meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017 Jan;33(1). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2818. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 27155214 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and Tolerability of the Intensification of Canagliflozin Dose from 100 mg to 300 mg Daily in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Real Life: The INTENSIFY Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 25;12(13):4248. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134248. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445283 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium and Hematocrit Levels' Correlation and Clinical Impacts in Jordanian Hemodialysis Patients.Cureus. 2024 Oct 10;16(10):e71208. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71208. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39525164 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Role of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Acute Heart Failure: From Pathophysiologic Mechanisms to Clinical Evidence with Pooled Analysis of Relevant Studies across Safety and Efficacy Endpoints of Interest.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 8;12(12):2062. doi: 10.3390/life12122062. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Empagliflozin on the Outcomes of β-Thalassemia Major in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The THALEMPA Observational Study.Cureus. 2024 Sep 21;16(9):e69837. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69837. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39435207 Free PMC article.
-
Masked anemia and hematocrit elevation under sodium glucose transporter inhibitors: findings from a large real-world study.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Jan;61(1):99-105. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02174-0. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 37698758
References
-
- Idris I, Donnelly R. Sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors: an emerging new class of oral antidiabetic drug. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11:79‐88. - PubMed
-
- Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117‐2128. - PubMed
-
- Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347‐357. - PubMed
-
- Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295‐2306. - PubMed
-
- Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:644‐657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

