Helminth infection is associated with dampened cytokine responses to viral and bacterial stimulations in Tsimane forager-horticulturalists
- PMID: 34868595
- PMCID: PMC8634526
- DOI: 10.1093/emph/eoab035
Helminth infection is associated with dampened cytokine responses to viral and bacterial stimulations in Tsimane forager-horticulturalists
Abstract
Background: Soil-transmitted helminths (STHs) and humans share long co-evolutionary histories over which STHs have evolved strategies to permit their persistence by downregulating host immunity. Understanding the interactions between STHs and other pathogens can inform our understanding of human evolution and contemporary disease patterns.
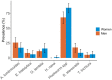
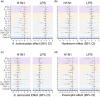
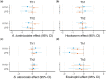
Methodology: We worked with Tsimane forager-horticulturalists in the Bolivian Amazon, where STHs are prevalent. We tested whether STHs and eosinophil levels-likely indicative of infection in this population-are associated with dampened immune responses to in vitro stimulation with H1N1 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antigens. Whole blood samples (n = 179) were treated with H1N1 vaccine and LPS and assayed for 13 cytokines (INF-γ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, GM-CSF and TNF-ɑ). We evaluated how STHs and eosinophil levels affected cytokine responses and T helper (Th) 1 and Th2-cytokine suite responses to stimulation.
Results: Infection with Ascaris lumbricoides was significantly (P ≤ 0.05) associated with lower response of some cytokines to H1N1 and LPS in women. Eosinophils were significantly negatively associated with some cytokine responses to H1N1 and LPS, with the strongest effects in women, and associated with a reduced Th1- and Th2-cytokine response to H1N1 and LPS in women and men.
Conclusions and implications: Consistent with the 'old friends' and hygiene hypotheses, we find that STHs were associated with dampened cytokine responses to certain viral and bacterial antigens. This suggests that STH infections may play an essential role in immune response regulation and that the lack of STH immune priming in industrialized populations may increase the risk of over-reactive immunity. Lay Summary: Indicators of helminth infection were associated with dampened cytokine immune responses to in vitro stimulation with viral and bacterial antigens in Tsimane forager-horticulturalists in the Bolivian Amazon, consistent with the 'old friends' and hygiene hypotheses.
Keywords: bacteria; cytokine storms; eosinophilia; hygiene hypothesis; hypereosinophilia; immunomodulation; old friends hypothesis; soil-transmitted helminths; viruses.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Foundation for Evolution, Medicine, and Public Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Old friends meet a new foe: A potential role for immune-priming parasites in mitigating COVID-19 morbidity and mortality.Evol Med Public Health. 2020 Oct 20;2020(1):234-248. doi: 10.1093/emph/eoaa037. eCollection 2020. Evol Med Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33235797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective immunity elicited by the nematode-conserved As37 recombinant protein against Ascaris suum infection.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Feb 13;14(2):e0008057. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008057. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32053593 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between male testosterone and immune function in a pathogenically stressed forager-horticultural population.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016 Nov;161(3):494-505. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23054. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016. PMID: 27465811 Free PMC article.
-
Soil-transmitted helminth infection and intestinal inflammation among the Shuar of Amazonian Ecuador.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2019 Sep;170(1):65-74. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23897. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2019. PMID: 31260090
-
The changes in the T helper 1 (Th1) and T helper 2 (Th2) cytokine balance during HIV-1 infection are indicative of an allergic response to viral proteins that may be reversed by Th2 cytokine inhibitors and immune response modifiers--a review and hypothesis.Virus Genes. 2004 Jan;28(1):5-18. doi: 10.1023/B:VIRU.0000012260.32578.72. Virus Genes. 2004. PMID: 14739648 Review.
Cited by
-
Poor Oral Health Is Associated With Inflammation, Aortic Valve Calcification, and Brain Volume Among Forager-Farmers.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 May 1;79(5):glae013. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae013. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38291985 Free PMC article.
-
Natural selection of immune and metabolic genes associated with health in two lowland Bolivian populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 3;120(1):e2207544120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2207544120. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36574663 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Ascaris infection modulates host immunity resulting in impaired control of Salmonella infection in pigs.mSphere. 2024 Sep 25;9(9):e0047824. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00478-24. Epub 2024 Aug 14. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39140728 Free PMC article.
-
A New Role for Old Friends: Effects of Helminth Infections on Vaccine Efficacy.Pathogens. 2022 Oct 8;11(10):1163. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101163. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36297220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal helminth infection impairs vaccine-induced T cell responses and protection against SARS-CoV-2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 15:2024.01.14.575588. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.14.575588. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Transl Med. 2024 Aug 21;16(761):eado1941. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ado1941. PMID: 38293221 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Yazdanbakhsh M, Kremsner PG, van Ree R.. Allergy, parasites, and the hygiene hypothesis. Science 2002;296:490–4. - PubMed

