Anticonstriction Effect of MCA in Rats by Danggui Buxue Decoction
- PMID: 34867357
- PMCID: PMC8634798
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.749915
Anticonstriction Effect of MCA in Rats by Danggui Buxue Decoction
Abstract
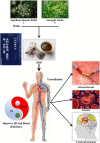
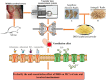
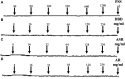
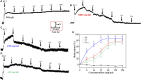
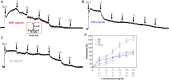
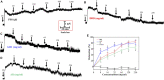
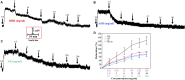
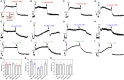
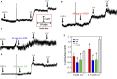
Objective: Danggui Buxue decoction (DBD), consisting of Angelicae Sinensis Radix (ASR) and Astragali Radix (AR), is a famous prescription with the function of antivasoconstriction. This study intends to probe its mechanisms on the relaxation of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Methods: Vascular tension of rat MCA was measured using a DMT620 M system. First, the identical series of concentrations of DBD, ASR, and AR were added into resting KCl and U46619 preconstricted MCA. According to the compatibility ratio, their dilatation effects were further investigated on KCl and U46619 preconstricted vessels. Third, four K+ channel blockers were employed to probe the vasodilator mechanism on KCl-contracted MCA. We finally examined the effects of DBD, ASR, and AR on the vascular tone of U46619-contracted MCA in the presence or absence of Ca2+. Results: Data suggested that DBD, ASR, and AR can relax on KCl and U46619 precontracted MCA with no effects on resting vessels. The vasodilator effect of ASR was greater than those of DBD and AR on KCl-contracted MCA. For U46619-contracted MCA, ASR showed a stronger vasodilator effect than DBD and AR at low concentrations, but DBD was stronger than ASR at high concentrations. Amazingly, the vasodilator effect of DBD was stronger than that of AR at all concentrations on two vasoconstrictors which evoked MCA. The vasodilator effect of ASR was superior to that of DBD at a compatibility ratio on KCl-contracted MCA at low concentrations, while being inferior to DBD at high concentrations. However, DBD exceeded AR in vasodilating MCA at all concentrations. For U46619-constricted MCA, DBD, ASR, and AR had almost identical vasodilation. The dilation of DBD and AR on KCl-contracted MCA was independent of K+ channel blockers. However, ASR may inhibit the K+ channel opening partially through synergistic interactions with Gli and BaCl2. DBD, ASR, and AR may be responsible for inhibiting [Ca2+]out, while ASR and AR can also inhibit [Ca2+]in. Conclusion: DBD can relax MCA with no effects on resting vessels. The mechanism may be related to ASR's inhibition of KATP and Kir channels. Meanwhile, the inhibition of [Ca2+]out by DBD, ASR, and AR as well as the inhibition of [Ca2+]in by ASR and AR may contribute to dilate MCA.
Keywords: Ca2+ channel; Danggui Buxue decoction; K+ channel; middle cerebral artery; vascular tone.
Copyright © 2021 Guo, Zhang, Hou, Guo, Wang, Zhang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The membrane permeability of Astragali Radix-derived formononetin and calycosin is increased by Angelicae Sinensis Radix in Caco-2 cells: a synergistic action of an ancient herbal decoction Danggui Buxue Tang.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012 Nov;70:671-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.05.018. Epub 2012 May 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012. PMID: 22704738
-
Exploring the immunometabolic potential of Danggui Buxue Decoction for the treatment of IBD-related colorectal cancer.Chin Med. 2024 Aug 29;19(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00978-y. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39210410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid chemical characterization of Danggui Buxue decoction using processed Astragali Radix and Angelicae Sinensis Radix based on diagnostic ion and molecular network.Biomed Chromatogr. 2023 Aug;37(8):e5640. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5640. Epub 2023 Apr 23. Biomed Chromatogr. 2023. PMID: 37013366
-
Metabolomics and molecular docking to compare of the efficacies of wild-simulated and transplanted Astragali Radix based on its compatibility with Angelicae Sinensis Radix against blood deficiency.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021 Apr 8;1173:122682. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122682. Online ahead of print. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33878534
-
Calycosin orchestrates the functions of Danggui Buxue Tang, a Chinese herbal decoction composing of Astragali Radix and Angelica Sinensis Radix: An evaluation by using calycosin-knock out herbal extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Jun 20;168:150-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25796405 Review.
Cited by
-
Danggui-Buxue decoction alleviated vascular senescence in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia through activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):1041-1053. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2230753. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37431236 Free PMC article.
-
Danggui Buxue decoction alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced myelosuppression by regulating β-hydroxybutyric acid metabolism and suppressing oxidative stress.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):710-721. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2201606. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37096658 Free PMC article.
-
Coumarins with Different Substituents from Leonurus japonicus Have Opposite Effects on Uterine Smooth Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 21;25(18):10162. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810162. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cainzos-Achirica M., Miedema M. D., McEvoy J. W., Al Rifai M., Greenland P., Dardari Z., et al. (2020). Coronary Artery Calcium for Personalized Allocation of Aspirin in Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in 2019: The MESA Study (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). Circulation 141, 1541–1553. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.045010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen X. Y., Wang Z. C., Guo C. X., Wang L. N. (2017). Preventive and Treatment Effect of Danggui Buxuetang and Liuwei Dihuang Tang on Early Hypertensive Renal Damage. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 23, 190–195. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017090190 - DOI
-
- Chen Y., Tao Y. Y., Li F. H. (2008). Effects of Danggui Buxue Decoction on Liver Fibrosis and Hepatic Lipid Peroxidation in Rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 28, 39–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

