Conductive Biomaterials as Bioactive Wound Dressing for Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 34859323
- PMCID: PMC8639891
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-021-00751-y
Conductive Biomaterials as Bioactive Wound Dressing for Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering
Abstract
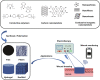
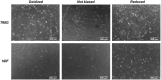
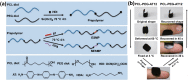
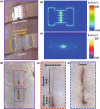
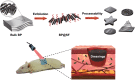
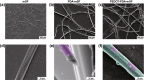
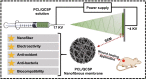
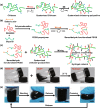
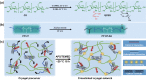
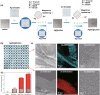
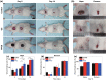
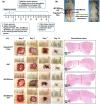
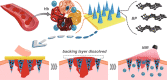
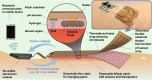
Conductive biomaterials based on conductive polymers, carbon nanomaterials, or conductive inorganic nanomaterials demonstrate great potential in wound healing and skin tissue engineering, owing to the similar conductivity to human skin, good antioxidant and antibacterial activities, electrically controlled drug delivery, and photothermal effect. However, a review highlights the design and application of conductive biomaterials for wound healing and skin tissue engineering is lacking. In this review, the design and fabrication methods of conductive biomaterials with various structural forms including film, nanofiber, membrane, hydrogel, sponge, foam, and acellular dermal matrix for applications in wound healing and skin tissue engineering and the corresponding mechanism in promoting the healing process were summarized. The approaches that conductive biomaterials realize their great value in healing wounds via three main strategies (electrotherapy, wound dressing, and wound assessment) were reviewed. The application of conductive biomaterials as wound dressing when facing different wounds including acute wound and chronic wound (infected wound and diabetic wound) and for wound monitoring is discussed in detail. The challenges and perspectives in designing and developing multifunctional conductive biomaterials are proposed as well.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Conducting polymers; Electrotherapy; Inorganic nanomaterials; Wound monitoring.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antibacterial biomaterials for skin wound dressing.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022 May;17(3):353-384. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.01.001. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35782328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan/Hyaluronic acid/Alginate and an assorted polymers loaded with honey, plant, and marine compounds for progressive wound healing-Know-how.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Sep 1;186:656-685. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.067. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34271047 Review.
-
Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing.ACS Nano. 2021 Aug 24;15(8):12687-12722. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c04206. Epub 2021 Aug 10. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 34374515 Review.
-
A review of the current state of natural biomaterials in wound healing applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 27;12:1309541. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1309541. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38600945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mussel-inspired, antibacterial, conductive, antioxidant, injectable composite hydrogel wound dressing to promote the regeneration of infected skin.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Nov 15;556:514-528. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.08.083. Epub 2019 Aug 24. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 31473541
Cited by
-
Conducting polymer hydrogels for biomedical application: Current status and outstanding challenges.APL Bioeng. 2024 Sep 24;8(3):031503. doi: 10.1063/5.0218251. eCollection 2024 Sep. APL Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 39323539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent research advances on corrosion mechanism and protection, and novel coating materials of magnesium alloys: a review.RSC Adv. 2023 Mar 14;13(12):8427-8463. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07829e. eCollection 2023 Mar 8. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36926015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in regenerative biomaterials.Regen Biomater. 2022 Dec 5;9:rbac098. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac098. eCollection 2022. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36518879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of Natural-Polymer-Based Hydrogels for Wound Antibacterial Therapeutics.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;15(15):3305. doi: 10.3390/polym15153305. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial biomaterials for skin wound dressing.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022 May;17(3):353-384. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.01.001. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35782328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
