Synthetic Cells: From Simple Bio-Inspired Modules to Sophisticated Integrated Systems
- PMID: 34856047
- PMCID: PMC9314110
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202110855
Synthetic Cells: From Simple Bio-Inspired Modules to Sophisticated Integrated Systems
Abstract
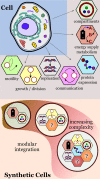
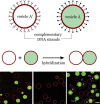
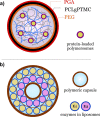
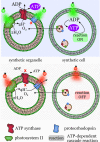
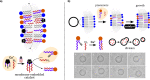
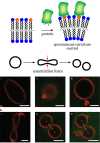
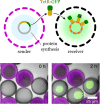
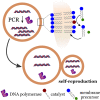
Bottom-up synthetic biology is the science of building systems that mimic the structure and function of living cells from scratch. To do this, researchers combine tools from chemistry, materials science, and biochemistry to develop functional and structural building blocks to construct synthetic cell-like systems. The many strategies and materials that have been developed in recent decades have enabled scientists to engineer synthetic cells and organelles that mimic the essential functions and behaviors of natural cells. Examples include synthetic cells that can synthesize their own ATP using light, maintain metabolic reactions through enzymatic networks, perform gene replication, and even grow and divide. In this Review, we discuss recent developments in the design and construction of synthetic cells and organelles using the bottom-up approach. Our goal is to present representative synthetic cells of increasing complexity as well as strategies for solving distinct challenges in bottom-up synthetic biology.
Keywords: artificial cells; artificial organelles; cell mimics; microreactors; synthetic biology.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mastering Complexity: Towards Bottom-up Construction of Multifunctional Eukaryotic Synthetic Cells.Trends Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;36(9):938-951. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.03.008. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Trends Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29685820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Micro/Nanoreactors toward the Creation of Artificial Organelles.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Mar;7(5). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700917. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29205928 Review.
-
Bottom-Up Assembly of Functional Intracellular Synthetic Organelles by Droplet-Based Microfluidics.Small. 2020 Jul;16(27):e1906424. doi: 10.1002/smll.201906424. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Small. 2020. PMID: 32078238
-
Artificial Cells: Synthetic Compartments with Life-like Functionality and Adaptivity.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Apr 18;50(4):769-777. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00512. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28094501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building a community to engineer synthetic cells and organelles from the bottom-up.Elife. 2021 Dec 20;10:e73556. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73556. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34927583 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Engineering a nanoscale liposome-in-liposome for in situ biochemical synthesis and multi-stage release.Nat Chem. 2024 Oct;16(10):1612-1620. doi: 10.1038/s41557-024-01584-z. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Nat Chem. 2024. PMID: 39009794 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically programmed synthetic cells for thermo-responsive protein synthesis and cargo release.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Oct;20(10):1380-1386. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01673-7. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38969863 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic asymmetric bacterial membranes incorporating lipopolysaccharides.Biophys J. 2023 Jun 6;122(11):2147-2161. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.12.017. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36523159 Free PMC article.
-
The hope, hype and obstacles surrounding cell therapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(10):e18359. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18359. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38770886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Encoding extracellular modification of artificial cell membranes using engineered self-translocating proteins.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 30;15(1):9363. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53783-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39477950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- None
-
- None
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

