Pentaglobin (immunoglobulin M-enriched immunoglobulin) as adjuvant therapy for premature and very low-birth-weight neonates with sepsis
- PMID: 34854404
- PMCID: PMC8641746
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_881_20
Pentaglobin (immunoglobulin M-enriched immunoglobulin) as adjuvant therapy for premature and very low-birth-weight neonates with sepsis
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this research was to determine the effectiveness of Pentaglobin® as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of sepsis in preterm newborns.
Materials and methods: It was a prospective, observational, randomized study for 272 premature neonates and very low birth weight (VLBW) that were diagnosed with sepsis carried at neonatal intensive care units. The patients randomized into control group who received standard sepsis antibiotic treatments, and an intervention group who received Pentaglobin® 5 ml/kg daily for 3 consecutive days as an adjunct therapy to a standard sepsis antibiotic treatment.
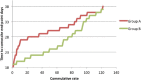
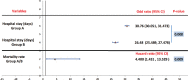
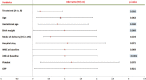
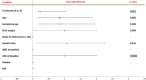
Results: Multiple organisms that isolated from culture specimens were Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive, and candida (56.25%, 42.28%, and 1.47%, respectively). The disease duration was distinctively longer in patients who were treated by the standard antibiotic protocol (mean ± standard deviation [SD]: 30.76 ± 3.97, odds ratio [OR]: 30.76, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 30.051, 31.473) comparing to the patients who received Pentaglobin adjuvant therapy (mean ± SD: 26.48 ± 5.55, OR: 26.48, 95% CI: 25.489, 27.477) (P < 0.000). Patients treated by standard antibiotic protocol were associated to a substantially increased risk of death (11.76%, hazard ratio 4.400, 95% CI: 1.432, 13.529, P = 0.009).
Conclusion: Neonatal sepsis is more common in premature and VLBW newborns, and Pentaglobin® management of newborn nosocomial sepsis might be used in addition to other therapies.
Keywords: Immunoglobulin M-enriched immunoglobulin; neonate; premature; sepsis; very low birth weight.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pentoxifylline and Pentaglobin adjuvant therapies for neonatal nosocomial sepsis in neonates less than 1500g weight.J Pak Med Assoc. 2017 Oct;67(10):1482-1486. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28955060
-
Pentaglobin as an adjunct therapy in very low birthweight neonates with nosocomial sepsis.J Pak Med Assoc. 2013 Nov;63(11):1353-7. J Pak Med Assoc. 2013. PMID: 24392518 Clinical Trial.
-
Are IgM-enriched immunoglobulins an effective adjuvant in septic VLBW infants?Ital J Pediatr. 2013 Oct 7;39:63. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-39-63. Ital J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 24098953 Free PMC article.
-
The use of IgM-enriched immunoglobulin in adult patients with sepsis.J Crit Care. 2018 Oct;47:30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.06.005. Epub 2018 Jun 3. J Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 29886064 Review.
-
Use of polyclonal immunoglobulins as adjunctive therapy for sepsis or septic shock.Crit Care Med. 2007 Dec;35(12):2677-85. Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 18074464 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of polyclonal and monoclonal based antibodies as promising potential therapy for treatment of sepsis: A systematic review.New Microbes New Infect. 2024 May 16;60-61:101435. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2024.101435. eCollection 2024 Aug-Oct. New Microbes New Infect. 2024. PMID: 38860003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis and Management of Neonatal Bacterial Sepsis: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 28;9(9):199. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9090199. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39330888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical efficacy of IgM-enriched immunoglobulin as adjunctive therapy in neonatal and pediatric sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2023 Aug 11;11:1239014. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1239014. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37635792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of IVIG therapy for patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 28;21(1):765. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04592-8. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37898763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiesa C, Panero A, Osborn JF, Simonetti AF, Pacifico L. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: A clinical and laboratory challenge. Clin Chem. 2004;50:279–87. - PubMed
-
- Parthasarathy A, Menon P, Nair M. IAP Textbook of Pediatrics. New Delhi: JP Medical Ltd; 2019.
-
- Cortese F, Scicchitano P, Gesualdo M, Filaninno A, De Giorgi E, Schettini F, et al. Early and late infections in newborns: Where do we stand? A review. Pediatr Neonatol. 2016;57:265–73. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Zhivaki D, Lo-Man R. Unique aspects of the perinatal immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:495–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical