Loss of DSTYK activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34853310
- PMCID: PMC8636471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-04385-1
Loss of DSTYK activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
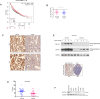
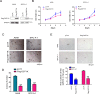
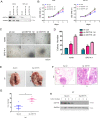
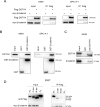
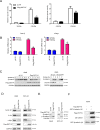
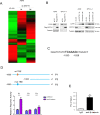
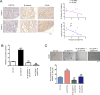
Aberrant activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and dysregulation of metabolism have been frequently observed in lung cancer. However, the molecular mechanism by which Wnt/β-catenin signaling is regulated and the link between Wnt/β-catenin signaling and cancer metabolism are not fully understood. In this study, we showed that the loss of dual serine/threonine tyrosine protein kinase (DSTYK) led to the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and upregulation of its target gene, lactate dehydrogenase (LDHA), and thus the elevation of lactate. DSTYK phosphorylated the N-terminal domain of β-catenin and inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which led to the inhibition of cell growth, colony formation and tumorigenesis in a lung adenocarcinoma mouse model. DSTYK was downregulated in lung cancer tissues, and its expression was positively correlated with the survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the loss of DSTYK activates Wnt/β-catenin/LDHA signaling to promote the tumorigenesis of lung cancer and that DSTYK may be a therapeutic target.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIF-1ɑ-regulated miR-1275 maintains stem cell-like phenotypes and promotes the progression of LUAD by simultaneously activating Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 22;10(6):2553-2570. doi: 10.7150/thno.41120. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32194819 Free PMC article.
-
Destrin Contributes to Lung Adenocarcinoma Progression by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Mol Cancer Res. 2020 Dec;18(12):1789-1802. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0187. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Mol Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32878967
-
RNA m6A reader YTHDF2 facilitates lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting the AXIN1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 13;12(5):479. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03763-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33980824 Free PMC article.
-
[Aerobic glycolysis activation through canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway in ALS].Med Sci (Paris). 2018 Apr;34(4):326-330. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20183404013. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Med Sci (Paris). 2018. PMID: 29658475 Review. French.
-
Dysregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by protein kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma and its therapeutic application.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):1695-1706. doi: 10.1111/cas.14861. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33605517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Significance and Expression Pattern of RIP5 and VGLL4 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Treated with Sunitinib.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 10;12(1):149. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010149. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255254 Free PMC article.
-
Temporin-GHaK Exhibits Antineoplastic Activity against Human Lung Adenocarcinoma by Inhibiting the Wnt Signaling Pathway through miRNA-4516.Molecules. 2024 Jun 12;29(12):2797. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122797. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930863 Free PMC article.
-
A novel anoikis-related gene signature to predict the prognosis, immune infiltration, and therapeutic outcome of lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Mar 31;15(3):1335-1352. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-149. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37065587 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrations in FGFR1, FGFR2, and RIP5 Expression in Human Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 8;23(24):15537. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415537. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555181 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the development and therapeutic resistance of non-small cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 13;22(1):565. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05380-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38872189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li F, Yang H, Kong T, Chen S, Li P, Chen L, et al. PGAM1, regulated by miR-3614-5p, functions as an oncogene by activating transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling in the progression of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:710. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02900-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

