Cyclin F drives proliferation through SCF-dependent degradation of the retinoblastoma-like tumor suppressor p130/RBL2
- PMID: 34851822
- PMCID: PMC8670743
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70691
Cyclin F drives proliferation through SCF-dependent degradation of the retinoblastoma-like tumor suppressor p130/RBL2
Abstract
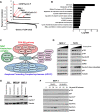
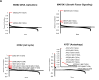
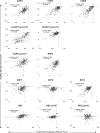
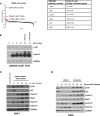
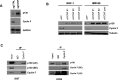
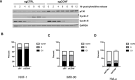
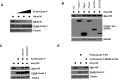
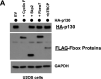
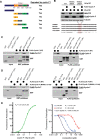
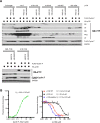
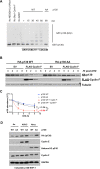
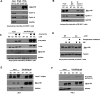
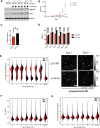
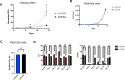
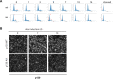
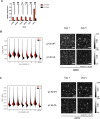
Cell cycle gene expression programs fuel proliferation and are universally dysregulated in cancer. The retinoblastoma (RB)-family of proteins, RB1, RBL1/p107, and RBL2/p130, coordinately represses cell cycle gene expression, inhibiting proliferation, and suppressing tumorigenesis. Phosphorylation of RB-family proteins by cyclin-dependent kinases is firmly established. Like phosphorylation, ubiquitination is essential to cell cycle control, and numerous proliferative regulators, tumor suppressors, and oncoproteins are ubiquitinated. However, little is known about the role of ubiquitin signaling in controlling RB-family proteins. A systems genetics analysis of CRISPR/Cas9 screens suggested the potential regulation of the RB-network by cyclin F, a substrate recognition receptor for the SCF family of E3 ligases. We demonstrate that RBL2/p130 is a direct substrate of SCFcyclin F. We map a cyclin F regulatory site to a flexible linker in the p130 pocket domain, and show that this site mediates binding, stability, and ubiquitination. Expression of a mutant version of p130, which cannot be ubiquitinated, severely impaired proliferative capacity and cell cycle progression. Consistently, we observed reduced expression of cell cycle gene transcripts, as well a reduced abundance of cell cycle proteins, analyzed by quantitative, iterative immunofluorescent imaging. These data suggest a key role for SCFcyclin F in the CDK-RB network and raise the possibility that aberrant p130 degradation could dysregulate the cell cycle in human cancers.
Keywords: RBL2/p130; SCF; cancer biology; cell biology; cell cycle; cyclin F; human; retinoblastoma; ubiquitin.
© 2021, Enrico et al.
Conflict of interest statement
TE, WS, EW, PN, XW, SR, NB, JP, ME No competing interests declared
Figures

Similar articles
-
RBL2/p130 is a direct AKT target and is required to induce apoptosis upon AKT inhibition in lung cancer and mesothelioma cell lines.Oncogene. 2018 Jul;37(27):3657-3671. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0214-3. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29606701
-
Expression and activity of the retinoblastoma protein (pRB)-family proteins, p107 and p130, during L6 myoblast differentiation.Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Oct;6(10):1287-98. Cell Growth Differ. 1995. PMID: 8845306
-
Human cytomegalovirus-encoded viral cyclin-dependent kinase (v-CDK) UL97 phosphorylates and inactivates the retinoblastoma protein-related p107 and p130 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 21;292(16):6583-6599. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773150. Epub 2017 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28289097 Free PMC article.
-
From G0 to S phase: a view of the roles played by the retinoblastoma (Rb) family members in the Rb-E2F pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Dec 15;102(6):1400-4. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21609. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17979151 Review.
-
Activity of the retinoblastoma family proteins, pRB, p107, and p130, during cellular proliferation and differentiation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jun;31(3):237-71. doi: 10.3109/10409239609106585. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8817077 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis reveals a PLK1-dependent G2/M degradation program and a role for AKAP2 in coordinating the mitotic cytoskeleton.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114510. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114510. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39018246 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin F-EXO1 axis controls cell cycle-dependent execution of double-strand break repair.Sci Adv. 2024 Aug 9;10(32):eado0636. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ado0636. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39121215 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Vif disrupts phosphatase feedback regulation at the kinetochore, leading to a pronounced pseudo-metaphase arrest.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 25:2024.07.30.605839. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.30.605839. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39131328 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A synthetic lethal dependency on casein kinase 2 in response to replication-perturbing therapeutics in RB1-deficient cancer cells.Sci Adv. 2024 May 24;10(21):eadj1564. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj1564. Epub 2024 May 23. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38781347 Free PMC article.
-
Injury-induced Foxm1 expression in the mouse kidney drives epithelial proliferation by a cyclin F-dependent mechanism.JCI Insight. 2024 Jun 25;9(15):e175416. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.175416. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38916959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agostinetto E, Vian L, Caparica R, Bruzzone M, Ceppi M, Lambertini M, Pondé N, de Azambuja E. CDK4/6 inhibitors as adjuvant treatment for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ESMO Open. 2021;6:100091. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100091. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldi A, Esposito V. Differential Tissues and Expression in Primary Lung and in Normal Human Tissues and in Primary Lung Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 1997;3:1691–1697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

