Effect of breastfeeding on children's health and its relationship to NRAMP1 expression: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 34840765
- PMCID: PMC8606844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.103017
Effect of breastfeeding on children's health and its relationship to NRAMP1 expression: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
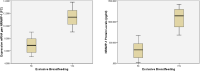
Toddlers with exclusive breastfeeding can increase immunity in preventing infectious diseases such as Upper Respiratory Tract Infections (ARI). The body's resistance to disease is controlled by Natural Resistance-Associated Macrophage Protein 1 (NRAMP1). NRAMP1 contributes to the pathophysiology of several intercellular infections, including ARI. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of breastfeeding on children's health and its relationship to NRAMP1 expression. A cross-sectional study was conducted on 124 toddlers in October 2020-June 2021. Toddlers were selected purposively from three Community Health Centers in Central Jakarta. The first group (n = 62) was exclusive breastfeeding and the second group (n = 62) was not exclusive breastfeeding. The characteristics of mothers and toddlers were collected using a structured questionnaire supported by medical record data. Meanwhile, NRAMP1 expression and NRAMP1 protein levels were obtained from the examination of blood samples. Examination of NRAMP1 gene mRNA expression by real-time PCR method and serum NRAMP1 protein levels by ELISA method. Data were analyzed using t-test, ANOVA, and multiple linear regression. The results obtained that the average mRNA expression of NRAMP1 gene and protein levels of NRAMP1 in infants who were not exclusive breastfeeding were 6.88 fold change (FC) and 315.02 pg/ml compared to those who received exclusive breastfeeding of 11.36 FC and 1087.74 pg./ml. Parity, immunization history, exclusive breastfeeding, and frequency of ARI were significantly associated with NRAMP1 gene mRNA expression and NRAMP1 protein levels (P < 0.05). Maternal and under-five age, gender, and nutritional status were not significantly related (P > 0.05). Exclusive breastfeeding was the dominant factor influencing NRAMP1 gene mRNA expression (OR: 4268) and NRAMP1 protein content (OR: 737,362). Antibodies obtained from exclusive breastfeeding in synergy with the NRAMP1 gene form the body's immunity in infants suffering from ARI.
Keywords: ARI; Exclusive breastfeeding; Immunization; NRAMP1 expression.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of exclusive breastfeeding on sIgA and lactoferrin levels in toddlers suffering from Acute Respiratory Infection: A cross-sectional study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Apr 26;77:103644. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103644. eCollection 2022 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35638033 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of ARI among Non-exclusively Breastfed Under-Five Passive Smoker Children: A Hospital-Based Cross-sectional Study of Nepal.Front Public Health. 2016 Feb 23;4:23. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2016.00023. eCollection 2016. Front Public Health. 2016. PMID: 26942173 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of factors influencing acute respiratory infection among under-five children in Sering Public Health Centre, Medan Tembung subdistrict.Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2021 Apr 30;63(2):228-233. doi: 10.3897/folmed.63.e52883. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2021. PMID: 33932013
-
Nutrition: basis for healthy children and mothers in Bangladesh.J Health Popul Nutr. 2008 Sep;26(3):325-39. doi: 10.3329/jhpn.v26i3.1899. J Health Popul Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18831228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early additional food and fluids for healthy breastfed full-term infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 25;(11):CD006462. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006462.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 30;(8):CD006462. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006462.pub4 PMID: 25420475 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of natural resistance-associated macrophage protein-1 (NRAMP-1) level based on death, comorbidities and severity of COVID-19 patients: a cross-sectional study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 May 12;85(6):2587-2591. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000830. eCollection 2023 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37363504 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of undernutrition using the composite index of anthropometric failure (CIAF) and its determinants: A cross-sectional study in the rural area of the Bogor District in Indonesia.BMC Nutr. 2022 Nov 16;8(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00627-3. BMC Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36384860 Free PMC article.
-
The role of exclusive breastfeeding on sIgA and lactoferrin levels in toddlers suffering from Acute Respiratory Infection: A cross-sectional study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Apr 26;77:103644. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103644. eCollection 2022 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35638033 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between oxytocin levels with empathy and breastfeeding intention in female medical students: A cross-sectional study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Aug 28;81:104486. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104486. eCollection 2022 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36147160 Free PMC article.
-
HbpA from Glaesserella parasuis induces an inflammatory response in 3D4/21 cells by activating the MAPK and NF-κB signalling pathways and protects mice against G. parasuis when used as an immunogen.Vet Res. 2024 Jul 29;55(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01344-4. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39075605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO and UNICEF . 2017. Global Breastfeeding Scorecard, 2017: Tracking progress for breastfeeding policies and programmes.
-
- Kemenkes R.I. ” Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan; Jakarta: 2019. Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2018.
-
- WHO . 2008. Indicators for Assessing Infant and Young Child Feeding Practices Part I.
-
- Permatasari T.A.E., et al. Exclusive breastfeeding intention among pregnant women. Kesmas. 2018;12(3):134–141. doi: 10.21109/kesmas.v12i3.1446. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials