With or without You: Co-Chaperones Mediate Health and Disease by Modifying Chaperone Function and Protein Triage
- PMID: 34831344
- PMCID: PMC8619055
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10113121
With or without You: Co-Chaperones Mediate Health and Disease by Modifying Chaperone Function and Protein Triage
Abstract
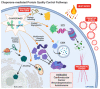
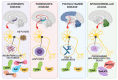
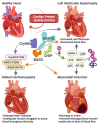
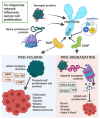
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are a family of molecular chaperones that regulate essential protein refolding and triage decisions to maintain protein homeostasis. Numerous co-chaperone proteins directly interact and modify the function of HSPs, and these interactions impact the outcome of protein triage, impacting everything from structural proteins to cell signaling mediators. The chaperone/co-chaperone machinery protects against various stressors to ensure cellular function in the face of stress. However, coding mutations, expression changes, and post-translational modifications of the chaperone/co-chaperone machinery can alter the cellular stress response. Importantly, these dysfunctions appear to contribute to numerous human diseases. Therapeutic targeting of chaperones is an attractive but challenging approach due to the vast functions of HSPs, likely contributing to the off-target effects of these therapies. Current efforts focus on targeting co-chaperones to develop precise treatments for numerous diseases caused by defects in protein quality control. This review focuses on the recent developments regarding selected HSP70/HSP90 co-chaperones, with a concentration on cardioprotection, neuroprotection, cancer, and autoimmune diseases. We also discuss therapeutic approaches that highlight both the utility and challenges of targeting co-chaperones.
Keywords: cancer; cardioprotection; co-chaperones; heat shock proteins; neuroprotection; protein degradation; protein folding; protein quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting Chaperone/Co-Chaperone Interactions with Small Molecules: A Novel Approach to Tackle Neurodegenerative Diseases.Cells. 2021 Sep 29;10(10):2596. doi: 10.3390/cells10102596. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the Heat Shock Protein System of Human Obligate Protozoan Parasites.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 25;20(23):5930. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235930. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31775392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock proteins in cell signaling and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022 Mar;1869(3):119187. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.119187. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 34906617 Review.
-
Modulation of protein fate decision by small molecules: targeting molecular chaperone machinery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Oct;10(10):1904-1925. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.01.018. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33163343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaperone families and interactions in metazoa.Essays Biochem. 2016 Oct 15;60(2):237-253. doi: 10.1042/EBC20160004. Essays Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27744339 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevation of major constitutive heat shock proteins is heat shock factor independent and essential for establishment and growth of Lgl loss and Yorkie gain-mediated tumors in Drosophila.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2022 Jul;27(4):431-448. doi: 10.1007/s12192-022-01283-z. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2022. PMID: 35704239 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Heat Shock Protein 70 Subfamily in the Hyperplastic Prostate: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities.Cells. 2022 Jun 28;11(13):2052. doi: 10.3390/cells11132052. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular chaperone networks and the export of J-domain proteins.J Biol Chem. 2023 Feb;299(2):102840. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102840. Epub 2022 Dec 26. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36581212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAG Family Members as Mitophagy Regulators in Mammals.Cells. 2022 Feb 15;11(4):681. doi: 10.3390/cells11040681. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jackson S.E. Hsp90: Structure and Function. In: Jackson S., editor. Molecular Chaperones. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2013. pp. 155–240. Topics in Current Chemistry.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

