Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Osteoarthritis Treatment: Extracellular Matrix Protection, Chondrocyte and Osteocyte Physiology, Pain and Inflammation Management
- PMID: 34831109
- PMCID: PMC8616200
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10112887
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Osteoarthritis Treatment: Extracellular Matrix Protection, Chondrocyte and Osteocyte Physiology, Pain and Inflammation Management
Abstract
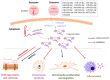
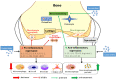
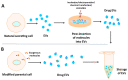
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative disease that can lead to persistent pain and motion restriction. In the last decade, stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have been explored as a potential alternative OA therapy due to their regenerative capacity. Furthermore, it has been shown that trophic factors enveloped in extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, are a crucial aspect of MSC-based treatment for OA. Evidently, EVs derived from different MSC sources might rescue the OA phenotype by targeting many biological processes associated with cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and exerting protective effects on different joint cell types. Despite this advancement, different studies employing EV treatment for OA have revealed reverse outcomes depending on the EV cargo, cell source, and pathological condition. Hence, in this review, we aim to summarize and discuss the possible effects of MSC-derived EVs based on recent findings at different stages of OA development, including effects on cartilage ECM, chondrocyte biology, osteocytes and bone homeostasis, inflammation, and pain management. Additionally, we discuss further strategies and technical advances for manipulating EVs to specifically target OA to bring the therapy closer to clinical use.
Keywords: bone homeostasis; chondrocytes; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; mesenchymal stem cells; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cartilage progenitor cells derived extracellular vesicles-based cell-free strategy for osteoarthritis treatment by efficient inflammation inhibition and extracellular matrix homeostasis restoration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 19;22(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02632-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38890638 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles as a potentially more beneficial therapeutic strategy than MSC-based treatment in a mild metabolic osteoarthritis model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 May 24;14(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03368-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37226203 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate chondrocyte damage during osteoarthritis through microRNA-130b-3p-mediated inhibition of the LRP12/AKT/β-catenin axis.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022 Apr;44(2):247-260. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2038192. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022. PMID: 35174753
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Potential Treatments for Osteoarthritis.Cells. 2021 May 22;10(6):1287. doi: 10.3390/cells10061287. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34067325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of articular degeneration by extracellular vesicles from stem/stromal cells as a potential strategy for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;228:116226. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116226. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38663683 Review.
Cited by
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes vs. Matrix-Bound Nanovesicles from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Osteoarthritis Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 28;25(21):11564. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111564. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519121 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends in extracellular vesicles based on stem cells from 1991 to 2021: A bibliometric and visualized study.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 30;10:956058. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.956058. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36110319 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by TGFβ-Stimulated Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Skin Fibroblasts by Promoting Fibroblast Migration and ECM Protein Production.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 27;10(8):1810. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081810. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009357 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells - a novel therapeutic tool in infectious diseases.Inflamm Regen. 2023 Feb 28;43(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s41232-023-00266-6. Inflamm Regen. 2023. PMID: 36849892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoarthritis rat serum-derived extracellular vesicles aggravate osteoarthritis development by inducing NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic cell death and cellular inflammation.Hum Cell. 2024 Nov;37(6):1624-1637. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01119-1. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 39141224
References
-
- Sen R.H.J. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2021. Osteoarthritis.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

