Doxorubicin-Resistant TNBC Cells Exhibit Rapid Growth with Cancer Stem Cell-like Properties and EMT Phenotype, Which Can Be Transferred to Parental Cells through Autocrine Signaling
- PMID: 34830320
- PMCID: PMC8623267
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212438
Doxorubicin-Resistant TNBC Cells Exhibit Rapid Growth with Cancer Stem Cell-like Properties and EMT Phenotype, Which Can Be Transferred to Parental Cells through Autocrine Signaling
Abstract
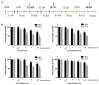
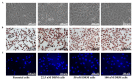
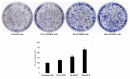
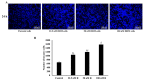
Emerging evidence suggests that breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs), and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) may be involved in resistance to doxorubicin. However, it is unlear whether the doxorubicin-induced EMT and expansion of BCSCs is related to cancer dormancy, or outgrowing cancer cells with maintaining resistance to doxorubicin, or whether the phenotypes can be transferred to other doxorubicin-sensitive cells. Here, we characterized the phenotype of doxorubicin-resistant TNBC cells while monitoring the EMT process and expansion of CSCs during the establishment of doxorubicin-resistant MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells (DRM cells). In addition, we assessed the potential signaling associated with the EMT process and expansion of CSCs in doxorubicin-resistance of DRM cells. DRM cells exhibited morphological changes from spindle-shaped MDA-MB-231 cells into round-shaped giant cells. They exhibited highly proliferative, EMT, adhesive, and invasive phenotypes. Molecularly, they showed up-regulation of Cyclin D1, mesenchymal markers (β-catenin, and N-cadherin), MMP-2, MMP-9, ICAM-1 and down-regulation of E-cadherin. As the molecular mechanisms responsible for the resistance to doxorubicin, up-regulation of EGFR and its downstream signaling, were suggested. AKT and ERK1/2 expression were also increased in DRM cells with the advancement of resistance to doxorubicin. Furthermore, doxorubicin resistance of DRM cells can be transferred by autocrine signaling. In conclusion, DRM cells harbored EMT features with CSC properties possessing increased proliferation, invasion, migration, and adhesion ability. The doxorubicin resistance, and doxorubicin-induced EMT and CSC properties of DRM cells, can be transferred to parental cells through autocrine signaling. Lastly, this feature of DRM cells might be associated with the up-regulation of EGFR.
Keywords: CSCs; EGFR; MDA-MB-231; breast cancer; doxorubicin-resistant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-EMT properties of CoQ0 attributed to PI3K/AKT/NFKB/MMP-9 signaling pathway through ROS-mediated apoptosis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 8;38(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1196-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31068208 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead Box Protein C2 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration and Invasion in Cisplatin-Resistant Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Line (SKOV3/CDDP).Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(3):1098-110. doi: 10.1159/000447818. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27562816
-
Inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor signalling potentiates mesenchymal-epithelial transition of breast cancer stem cells and their responsiveness to anticancer drugs.FEBS J. 2017 Jun;284(12):1830-1854. doi: 10.1111/febs.14084. Epub 2017 May 16. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28398698
-
The correlation between cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: molecular mechanisms and significance in cancer theragnosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 30;15:1417201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1417201. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39403386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addiction of Cancer Stem Cells to MUC1-C in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 26;23(15):8219. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158219. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897789 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tocopherol-human serum albumin nanoparticles enhance lapatinib delivery and overcome doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024 Jul 2;19(16):1431-1448. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2359357. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38953854
-
Molecular Research and Treatment of Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 25;23(17):9617. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179617. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077013 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine Motility Factor and Its Peptide Derivative Inhibit Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Regulating Wound Repair, Survival, and Drug Efflux.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 31;25(21):11714. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111714. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519266 Free PMC article.
-
Piperine enhances doxorubicin sensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and cancer stem cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 6;14(1):18181. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65508-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39107323 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning identifies heterogeneous subpopulations in breast cancer cell lines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 4:2024.07.02.601576. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.02.601576. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39005432 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

