Terretonin as a New Protective Agent against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury: Impact on SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κBp65/NLRP3 Signaling
- PMID: 34827212
- PMCID: PMC8614783
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10111219
Terretonin as a New Protective Agent against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury: Impact on SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κBp65/NLRP3 Signaling
Abstract
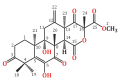
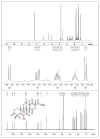
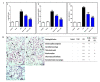
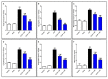
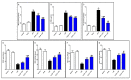
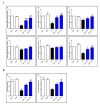
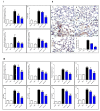
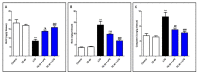
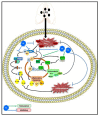
Endophytic fungi are proving to be an excellent source of chemical entities with unique structures and varied bioactivities. Terretonin (TE) and its structurally related derivatives are a class of meroterpenoids, possessing the same unique tetracyclic core skeleton, which have been reported from the Aspergillus genus. This study was carried out to assess the potential protective effects of TE separated from the endophytic fungus A. terreus against LPS (lipopolysaccharide)-induced ALI (acute lung injury) in mice. The results revealed that TE alleviated pulmonary edema as it lowered both the W/D lung ratio and protein content. The inflammatory response represented by inflammatory cell infiltration into the lung tissues was greatly repressed by TE. That was supported by the improved histopathological results and also by the reduced level of myeloperoxidase in the lung. TE showed a potent antioxidant activity as it attenuated lipid peroxidative markers (malondialdehyde, 4-hydroxynonenal, and protein carbonyl) and enhanced endogenous antioxidants (reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) in lung tissues. Similarly, TE increased the mRNA expression of SIRT1, Nrf2, and its genes (HO-1, NQO1, and GCLm). On the other hand, TE restrained the activation of NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB) in the lung. Consequently, TE depressed the pro-inflammatory cytokines: nitric oxide (NOx), TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α), and interleukins (IL-6 and -1β). Additionally, TE inhibited NLRP3 signaling and interrupted apoptosis by decreasing the levels of proapoptotic markers (Bax and caspase-3) and increasing the level of an anti-apoptotic marker (Bcl-2). In conclusion, TE had a remarkable protective potential on LPS-induced lung damage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. This finding encourages further investigations on this promising candidate.
Keywords: Aspergillus terreus; LPS; NF-κB; Nrf2; anti-inflammatory; endophytic fungi; terretonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of kaempferol glucoside against lipopolysaccharide-caused acute lung injury via targeting Nrf2/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD: Integrating experimental and computational studies.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Jun;32(6):102073. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102073. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38681737 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Yam Glycoprotein on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via the NLRP3 and NF-κB/TLR4 signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106024. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106024. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31784404
-
Inhibition of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 signal axis in inhibition of NLRP3 activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Apr 30;551:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.009. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33713981
-
Protective anti-inflammatory activity of tovophyllin A against acute lung injury and its potential cytotoxicity to epithelial lung and breast carcinomas.Inflammopharmacology. 2020 Feb;28(1):153-163. doi: 10.1007/s10787-019-00609-1. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31218570
-
S-allylmercaptocysteine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via nuclear factor kappa B and Keap1/Nrf2 pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106273. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106273. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32070920
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of HUC-MSC-exos primed with IFN-γ against LPS-induced acute lung injury.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(3):375-382. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.74372.16156. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38333754 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the AMPK/Nrf2 Pathway: A Novel Therapeutic Approach for Acute Lung Injury.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 15;17:4683-4700. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S467882. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39051049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaetomugilins and Chaetoviridins-Promising Natural Metabolites: Structures, Separation, Characterization, Biosynthesis, Bioactivities, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;8(2):127. doi: 10.3390/jof8020127. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Docking and Molecular Dynamic Investigations of Phenylspirodrimanes as Cannabinoid Receptor-2 Agonists.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):44. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010044. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615238 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 Deficiency Exacerbated CLP-Induced Pulmonary Injury and Inflammation through Autophagy- and NF-κB/PPARγ-Mediated Macrophage Polarization.Cells. 2022 Dec 4;11(23):3927. doi: 10.3390/cells11233927. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ibrahim S.R.M., Ahmed N., Almalki S., Alharbi N., El-Agamy D.S., Alahmadi L.A., Saubr M.K., Elkablawy M., Elshafie R.M., Mohamed G.A., et al. Vitex agnus-castus safeguards the lung against lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity in mice. J. Food Biochem. 2019;43:e12750. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12750. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ammar E.A., Sharawy M.H., Shalaby A.A., El-Agamy D.S. Effects of methyl palmitate and lutein on LPS–induced acute lung injury in rats. World J. Respirol. 2013;3:20–28. doi: 10.5320/wjr.v3.i2.20. - DOI
-
- Ahmed N., Aljuhani N., Salamah S., Surrati H., El-Agamy D.S., Elkablawy M.A., Ibrahim S.R.M., Mohamed G.A. Pulicaria petiolaris effectively attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury in mice. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2018;70:699–706. doi: 10.2298/ABS180510033A. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

