The Anti-Cancer Effect of A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonists: A Novel, Targeted Therapy
- PMID: 34824647
- PMCID: PMC8611655
- DOI: 10.2174/187152207781369878
The Anti-Cancer Effect of A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonists: A Novel, Targeted Therapy
Abstract
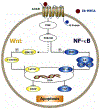
The A3 adenosine receptor (A3AR) is highly expressed in various human solid tumor cells whereas low expression is found in the adjacent normal tissues. Activation of the A3AR with synthetic highly selective agonists, such as IB-MECA, Cl-IB-MECA or LJ529, induces tumor growth inhibition of melanoma, lymphoma, breast, hepatoma, prostate and colon carcinoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Two molecular events take place upon receptor activation and include: a. receptor internalization and subsequent degradation, followed by decreased receptor mRNA and protein expression level. b. modulation of down-stream signal transduction pathways, including those related to Wnt and NF-κB. Subsequently, the levels of cyclin D1 and c-Myc are decreased leading to tumor growth inhibition. IB-MECA synergizes with chemotherapeutic agents to yield an additive anti-tumor effect and protects against myelotoxicity induced by chemotherapy. Taken together, A3AR agonists may be suggested as a new family of orally bioavailable compounds to be developed as potent inhibitors of malignant diseases.
Keywords: A3 Adenosine receptor; NF-κB.; PKB/Akt; Wnt; anti-cancer effect; synthetic agonists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The PI3K-NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway is involved in mediating the anti-inflammatory effect of IB-MECA in adjuvant-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(1):R33. doi: 10.1186/ar1887. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16507132 Free PMC article.
-
A3 adenosine receptor activation in melanoma cells: association between receptor fate and tumor growth inhibition.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 24;278(43):42121-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301243200. Epub 2003 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12865431
-
Targeting the A3 adenosine receptor for cancer therapy: inhibition of prostate carcinoma cell growth by A3AR agonist.Anticancer Res. 2003 May-Jun;23(3A):2077-83. Anticancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12894581
-
A3 adenosine receptor as a target for cancer therapy.Anticancer Drugs. 2002 Jun;13(5):437-43. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200206000-00001. Anticancer Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12045454 Review.
-
The anti-inflammatory effect of A3 adenosine receptor agonists: a novel targeted therapy for rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007 Oct;16(10):1601-13. doi: 10.1517/13543784.16.10.1601. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17922624 Review.
Cited by
-
2-Dialkynyl derivatives of (N)-methanocarba nucleosides: 'Clickable' A(3) adenosine receptor-selective agonists.Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Jan 15;18(2):508-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.12.018. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20036562 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalized congeners of A3 adenosine receptor-selective nucleosides containing a bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane ring system.J Med Chem. 2009 Dec 10;52(23):7580-92. doi: 10.1021/jm900426g. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19499950 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the A3 adenosine receptor to treat hepatocellular carcinoma: anti-cancer and hepatoprotective effects.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Sep;19(3):513-522. doi: 10.1007/s11302-023-09925-2. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 36781824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine receptors and cancer.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(193):399-441. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-89615-9_14. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19639290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of (N)-methanocarba adenosine 5'-uronamides as species-independent A3 receptor-selective agonists.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 May 1;18(9):2813-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 Apr 4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008. PMID: 18424135 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous